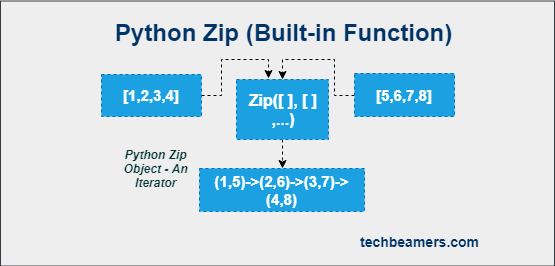
Python zip() is a versatile function that can be used to iterate over two or more iterables in parallel. It can create a list of tuples from two or more iterables or merge two dictionaries into a single dictionary. Let’s explore what else can we do using the zip() function in Python.
A brief intro to Python zip()
Python’s zip() function is used for merging and synchronizing multiple collections, such as lists, tuples, or strings, into a new sequence of tuples. It takes two or more iterables as input and returns a zip object. A zip object is a generator that produces tuples of corresponding elements from the iterables. The length of the zip object is the length of the shortest iterable. Here is the syntax:
zip(*iterables, **kwargs)
A short description of the arguments:
iterables: A sequence of iterables.fillvalue: A value to use to fill in the gaps if the iterables are not the same length.
Below are some of the popular variations of the Python zip function. Check these and learn how to use the zip function in Python.
Simple zip() function
zip(*iterables): This is the most common way to use the zip() function. It takes a sequence of iterables as input and returns a zip object. The following code creates a zip object from two lists:
list1 = [1, 2, 3] list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] zipped = zip(list1, list2) print(zipped)
The output of the code is a zip object. This object can be iterated over to produce tuples of corresponding elements from the two lists:
for item in zipped:
print(item)The output of the code is:
(1, 'a') (2, 'b') (3, 'c')
Passing a fill value
zip(*iterables, fillvalue=value): This variation of the Python zip function takes a sequence of iterables and fillvalue. The second argument specifies the value that should be used to fill in the gaps if the iterables are not the same length.
The following code uses the fill value argument to fill in the gaps in the zip object:
list1 = [1, 2, 3] list2 = ['a', 'b'] zipped = zip(list1, list2, fillvalue='x') print(zipped)
The output of the code is:
[(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'x')]
Returning a list of tuples
list(zip(*iterables)): This variation of the zip() function returns a list of tuples from the zip object.
The following code creates a list of tuples from two lists:
list1 = [1, 2, 3] list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] zipped = list(zip(list1, list2)) print(zipped)
The output of the code is:
[(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c')]
Here is a table that summarizes the different variations of the Python zip function and how to use them:
| Variation | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
zip(*iterables) | zip(list1, list2) | Returns a zip object from the iterables. |
zip(*iterables, fillvalue=value) | zip(list1, list2, fillvalue='x') | Returns a zip object from the iterables, filling in the gaps with the value value. |
list(zip(*iterables)) | list(zip(list1, list2)) | Returns a list of tuples from the zip object. |
By the way, we like to introduce here 100+ Python interview questions that is one of our most helpful resources for Python programmers. You should go through it once you complete this tutorial. It will certainly boost your understanding of various programming concepts.
Python zip() examples
The zip() function in Python is a versatile function and you can do many unique things with it. Here are a few examples:
Iterating over two or more lists in parallel
Zip() pairs elements at corresponding positions from multiple iterables, allowing for simultaneous iteration. It streamlines the processing of related data together. In this example, we have two lists, names, and ages, and we use zip() to pair names with their corresponding ages for easy printing.
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
ages = [25, 30, 22]
for name, age in zip(names, ages):
print(f"{name} is {age} years old.")
Merging two dictionaries
Python zip() can merge key-value pairs from two dictionaries, creating a new harmonious dictionary. In this example, we have two dictionaries, dict1, and dict2, and we use zip() to combine their key-value pairs into a new dictionary merged_dict.
dict1 = {'a': 1, 'b': 2}
dict2 = {'c': 3, 'd': 4}
merged_dict = dict(zip(dict1.keys(), dict2.values()))
print(merged_dict)
Transposing a matrix
Zip() transposes a 2D matrix by flipping rows and columns, seamlessly rearranging data. In this example, we have a 2D matrix, and we use zip(*matrix) to transpose it into transposed_matrix.
matrix = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
]
transposed_matrix = list(zip(*matrix))
print(transposed_matrix)
Sorting two or more lists together
Python zip can be used to sort two or more iterables together. In this example, we have two lists, names, and scores, and we use zip() to pair them together. We then use the Python sorted() function with reverse=True to sort the data based on scores in descending order.
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"] scores = [85, 92, 78] sorted_data = sorted(zip(scores, names), reverse=True) print(sorted_data)
Looping over multiple lists
Zip() helps iterate through names and scores simultaneously, pairing related data. In this example, we use zip() to combine names and scores and iterate them together, allowing us to print each person’s name along with their score.
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
scores = [85, 92, 78]
for name, score in zip(names, scores):
print(f"{name} scored {score} marks.")
Finding common elements
Zip() assists in discovering common elements between list1 and list2, pairing corresponding elements for comparison. In this example, we have two lists, list1, and list2, and we use zip() to pair their elements. We then convert the pairs into a set to find the common elements.
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] list2 = [3, 4, 5, 6] common_elements = set(zip(list1, list2)) print(common_elements)
Zip lists of different sizes
If the size of lists is different, the zip() function will only pair the elements up to the length of the shortest list. It will not include the remaining elements from the result.
For example, the following code will zip two lists of different lengths:
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] zipped = zip(list1, list2) print(zipped)
This code will print the following output:
[(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c')]
As you can see, the zip() function only paired up the first three elements of each list. The fourth element of list1 was ignored, and the third element of list2 was also ignored.
If you want to zip different-sized lists and include all of the elements, you can use the itertools.zip_longest() function. This function will pair up the elements of the lists as much as possible, and then it will fill in the remaining elements with None values. See the example below.
import itertools list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4] list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c'] zipped = itertools.zip_longest(list1, list2, fillvalue=None) print(zipped) # [(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c'), (None, None)]
However, we can even add actual elements instead of appending None. Check the updated example.
import itertools
list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']
extra_values = ['d', 'e', 'f']
zipped = itertools.zip_longest(list1, list2, fillvalue=extra_values)
print(zipped)
# [(1, 'a'), (2, 'b'), (3, 'c'), ('d', 'd'), ('e', 'e'), ('f', 'f')]
Summary
You are now aware that the Python zip() function can do multiple tasks. It can pair elements from multiple lists in parallel. It can be used to simplify data manipulation by making it easier to iterate over multiple lists, merge dictionaries, transpose matrices, and find common elements. Hence, without any doubt, we can say that the zip() function is a powerful tool for data processing in Python.