Python sorted function is a built-in method. As the name suggests, it provides the functionality to sort the objects of different data types. In this tutorial, We’ll demonstrate its usage to sort a string, list, tuple, and dictionary with examples.
Sorting is a time-critical operation for any application. It can directly affect performance and speed. You may like to use it in various scenarios such as ordering a user’s activity logs by timestamp or putting a list of customers in alphabetical order. Python’s sorting function enables basic sorting, but you can also change it as per the need.
Python Sorted Function Explained
This tutorial explains everything about the sorted function such as how to use it on different types, changing the sort order, and its comparison with the python’s sort list method.
The sorted() function takes a sequence (an iterable) as input and sorts its elements in the default ascending order. The return value is the original list with all its items intact but in the sorted order.
We can sort the iterable in a particular order, i.e., either ascending or descending. It sorts the strings alphabetically while the numbers get sorted in numerical order.
It is not possible to sort a sequence that includes mixed values such as strings and numbers.
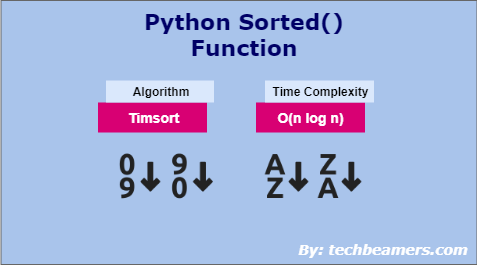
Python sorted() function uses Timsort algorithm and has O(n log n) time complexity.
Sorted function syntax
Python sorted function declaration is as follows:
sorted(iterable[, key = None][, reverse = False])
It allows three arguments from which “iterable” is mandatory and the rest two are optional. See more info on each of these below.
Iterable (Mandatory): It is the sequence you wish to sort. If you don’t specify any key, then sorting happens in the default order.
Key (Optional): It represents a function used for comparing the list elements during the sort operation.
Reverse (Optional): Another optional boolean argument, if you pass it as True, then sorting will happen in the reverse order.
Python sorted() function modifies the input list, sorts, and returns the updated list as an iterable.
Python sorted function example
Let’s sort an unordered list of alphabets using the sorted function.
sample_list = ("h", "d", "c", "a", "b", "e", "f", "g")
out_list = sorted(sample_list)
print(out_list)Output:
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h']
Using sorted function on basic data types
We can apply the sorted function to different types of iterables such as strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries.
Hence, we can use the Python sorted function on it. See the example below.
sample_str = ("Machine Learning")
out_str = sorted(sample_str)
print("Sorted output: ", out_str)
print("Ascii value of ' ': ", ord(' '))
print("Ascii value of 'L': ", ord('L'))
print("Ascii value of 'M': ", ord('M'))
print("Ascii value of 'a': ", ord('a'))Output:
Sorted output: [' ', 'L', 'M', 'a', 'a', 'c', 'e', 'e', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'i', 'n', 'n', 'n', 'r'] Ascii value of ' ': 32 Ascii value of 'L': 76 Ascii value of 'M': 77 Ascii value of 'a': 97
After printing the sorted function output, we displayed the ASCII values of a few of the letters in the input string. It is to show that sorting is happening based on the ASCII values of the individual character.
The following Python string tutorial will help you understand more about this topic.
Using sorted() to sort lists
The most common iterables in Python are list-type objects. Let’s go over a few examples of sorting Python lists.
sample_list = sorted(['X', '1', 'Z']) print(sample_list) sample_list = sorted(['X', '9Y', 'Z']) print(sample_list) sample_list = sorted(['A', 'a', 'b', 'B']) print(sample_list) sample_list = sorted([-5, 2, -3, 1, 0, -4, 4, -2, -1, 5]) print(sample_list)
Output:
['1', 'X', 'Z'] ['9Y', 'X', 'Z'] ['A', 'B', 'a', 'b'] [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 4, 5]
Do check out our detailed tutorial on the Python list.
Sort tuples using sorted()
Below is an example of a tuple sorted using the Python sorted() function.
sample_tup = sorted((10, 30, 20, -10, -20)) print(sample_tup) print(type(sample_tup))
Output:
[-20, -10, 10, 20, 30] <class 'list'>
You can see that the final output is a list.
Learn more about Python tuples here.
Sort a dictionary
A dictionary is a composite object which consists of a group of key-value pairs. Let’s see how to use the sorted() method to sort its elements.
sample_dict = {'function': 'sorted()', 'params': 3, 'arg1': 'iterable', 'arg2': 'key', 'arg3': 'reverse', 'return value': 'list'}
print(sample_dict)
print(sorted(sample_dict))Output:
{'function': 'sorted()', 'params': 3, 'arg1': 'iterable', 'arg2': 'key', 'arg3': 'reverse', 'return value': 'list'}
['arg1', 'arg2', 'arg3', 'function', 'params', 'return value']The dictionary values are sorted based on the “key” field. You can read more about the Python dictionary here.
Sort in reverse direction
Now, we’ll use the 2nd argument of the sorted function. Let’s see what impact does it have on the sorted output.
sample_str = ['Modi', 'Trump', 'Putin', 'Jinping']
print("Default sort: ", sorted(sample_str))
print("Reversed sort: ", sorted(sample_str, reverse = True))
sample_list = [5, 17, 37, 3, 13]
print("\nDefault sort: ", sorted(sample_list))
print("Reversed sort: ", sorted(sample_list, reverse = True))
sample_tup = (-1, -2, 2, 1, 0)
print("\nDefault sort: ", sorted(sample_tup))
print("Reversed sort: ", sorted(sample_tup, reverse = True))
sample_dict = {'function': 'sorted()', 'params': 3, 'arg1': 'iterable', 'arg2': 'key', 'arg3': 'reverse', 'return value': 'list'}
print("\nDefault sort: ", sorted(sample_dict))
print("Reversed sort: ", sorted(sample_dict, reverse = True))Output:
Default sort: ['Jinping', 'Modi', 'Putin', 'Trump'] Reversed sort: ['Trump', 'Putin', 'Modi', 'Jinping'] Default sort: [3, 5, 13, 17, 37] Reversed sort: [37, 17, 13, 5, 3] Default sort: [-2, -1, 0, 1, 2] Reversed sort: [2, 1, 0, -1, -2] Default sort: ['arg1', 'arg2', 'arg3', 'function', 'params', 'return value'] Reversed sort: ['return value', 'params', 'function', 'arg3', 'arg2', 'arg1']
Sort using key
We can also provide a third argument to the Python sorted function. It can help us change the way the default function works.
For example, by default, it sorts a string based on the ASCII values. We can alter it to sort based on the length of the literal.
sample_str = ['Modi', 'Trump', 'Putin', 'Jinping']
print("Default sort: ", sorted(sample_str))
# We are passing the built-in len() method as the sort key
print("Key-based sort: ", sorted(sample_str, key = len))Output:
Default sort: ['Jinping', 'Modi', 'Putin', 'Trump'] Key-based sort: ['Modi', 'Trump', 'Putin', 'Jinping']
Similarly, the sorted() function sorts a dictionary by its “key” field. With the sorted-key option, we can sort it based on the “value” field.
sample_dict = {'andi': 65, 'george': 34, 'elvis': 44, 'david': 25, 'caleb': 18, 'broady': 27}
print("\nDefault sort: ", sorted(sample_dict))
# Let's sort a dictionary by value
print("Key-based sort: ", sorted(sample_dict, key = lambda sample_dict: sample_dict[1]))Output:
Default sort: ['andi', 'broady', 'caleb', 'david', 'elvis', 'george'] Key-based sort: ['david', 'caleb', 'george', 'elvis', 'andi', 'broady']
We’ve used Python lambda in the above example. It is used to create a tiny anonymous function that operates inline.
Sorted() function on mixed data types
We’ve earlier told you that the sorted() function doesn’t support the sorting of mixed types. Let’s see what exactly happens when you call it on an iterable having distinct objects.
Check out the below example:
mixed_type_list = ['a', 1, 'x', -3] print(sorted(mixed_type_list))
Output:
TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'int' and 'str'
Sorted() vs. list sort()
There are some obvious differences between the two sort functions:
- The sorted() function is richer in functionality as it can sort iterable of any type given as input. The sort method is strictly for the list.
- Python sorted() function creates a new range object with the elements of the original list in the sorted order. The
List.sort()method does an in-place sorting and modifies the source list.
If you have multiple lists (e.g. employees and their salary lists) that you have to combine, Python zip is the function you should use.
How to sort a user-defined type?
You will be glad to learn that we can even use Python’s sorted function to sort lists containing custom types. To demonstrate this, we’ll create a sequence of student classes and sort them based on different criteria.
"""
Desc: Create a user-defined type
Name: Student class
"""
class Student:
name = ''
rollno = 0
section = ''
subject = ''
def __init__(self, nm, rn, sn, ss):
self.name = nm
self.rollno = rn
self.section = sn
self.subject = ss
def __str__(self):
return 'St[name=%s, rollno=%s, section=%s, subject=%s]' % (self.name, self.rollno, self.section, self.subject)
"""
Desc: Let's have a list of student objects as follows:
"""
st1 = Student('Saba', 1, '1A', 'EVS')
st2 = Student('Ila', 2, '1B', 'Science')
st3 = Student('Kim',3, '2A', 'Maths')
st4 = Student('Kim',4, '2B', 'GK')
stu_list = [st1, st2, st3, st4]
"""
Desc: Sorting list of students based on rollno
"""
def get_stu_rollno(st):
return st.rollno
stu_list_by_rollno = sorted(stu_list, key=get_stu_rollno)
print("List of students ordered by rollno: ")
for st in stu_list_by_rollno:
print(st)
"""
Desc: Sorting list of students based on section
"""
def get_stu_section(st):
return st.section
stu_list_by_section = sorted(stu_list, key=get_stu_section)
print("\nList of students ordered by section: ")
for st in stu_list_by_section:
print(st)Output:
List of students ordered by rollno: St[name=Saba, rollno=1, section=1A, subject=EVS] St[name=Ila, rollno=2, section=1B, subject=Science] St[name=Kim, rollno=3, section=2A, subject=Maths] St[name=Kim, rollno=4, section=2B, subject=GK] List of students ordered by section: St[name=Saba, rollno=1, section=1A, subject=EVS] St[name=Ila, rollno=2, section=1B, subject=Science] St[name=Kim, rollno=3, section=2A, subject=Maths] St[name=Kim, rollno=4, section=2B, subject=GK]
Must Read: Search Key in Dictionary
Summary
You’ve now sensed the power of the Python sorted function. And now it’s your turn to taste it by using it in real applications.
If you have any queries, do let us know. We wish you all the best.