Are you searching for the most important questions asked in testing interviews? Take a halt. Our team has curated 100+ manual testing interview questions that cover all aspects of manual testing, including test planning, test execution, defect management, and more. Each question is designed to upgrade your knowledge and skills, so you can confidently answer any questions asked. Let us ensure that you are hired for sure.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [General Testing]
Whether you’re a seasoned tester or just starting out, our guide is the ultimate resource for mastering manual testing interview questions. So what are you waiting for? Let’s get started!
What is Software Testing and what is its process?
Software testing is a validation process that confirms that a system works as per the business requirements. It qualifies a system on various aspects such as usability, accuracy, completeness, efficiency, etc. The ANSI/IEEE 1059 is the global standard that defines the basic principles of testing.
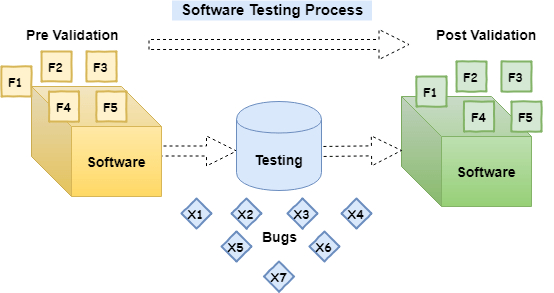
Why is Software Testing required?
It is a mandatory process that is essential to qualify software as usable for production. Here are some compelling reasons to prove why is it needed.
- The testing process guarantees the software will work as per the expectations of the customers.
- It reduces the coding cycles by identifying issues at the initial stage of development.
- The discovery of issues in the earlier SDLC phases ensures proper utilization of resources and prevents any cost escalations.
- The testing team brings the customer view into the process and finds use cases that a developer may overlook.
- Any failure, defect, or bug observed by the customer distorts a firm’s credibility. Only adequate testing can ensure it to not happen.
When should you start the testing process?
Testing should begin from the inception of the project. Once you get the requirements baselined, the System testing plan and test case preparation should start. It also helps in exploring any gaps in the functional requirements.
When should you stop the testing process?
The testing activity ends after the team completes the following milestones.
- Test case execution: The successful completion of a full test cycle after the final bug fix marks the end of the testing phase.
- Testing deadline: The end date of the validation stage also declares the closure of the validation if no critical or high-priority defects remain in the system.
- MTBF rate: It is the mean time between failures (MTBF), which reflects the reliability of the components. If it is on the higher side, then PO and EM can decide to stop testing.
- CC ratio: It is the amount of code covered via automated tests. If the team achieves the desired level of code coverage (CC) ratio, then they can choose to end the validation.
What does Quality Assurance mean in Software testing?
Quality Assurance is a process to certify the effectiveness and accuracy of software development (SDLC) method. It may bring changes in the process and cause to replace the weak practices if it identifies any. It includes review activities such as the inspection of documents, test cases, source code, automation, etc.
What does Quality Control mean in Software testing?
Quality control is a product-oriented approach to ensure that the product under development meets the original software specifications. It also results in changes to the product. For example – if there are bugs in the system or some deviation observed in the implementation. It includes different types of testing to perform, which are functional (unit, usability, integration, etc.) and non-functional (compatibility, security, performance, etc.).
What does Verification mean in Software testing?
In software testing, verification is a means to confirm that product development is taking place as per the specifications and using standard development procedures. It comprises the following activities.
- Inspections
- Reviews
- Walk-throughs
- Demos
What does Validation mean in Software testing?
In software testing, validation is a means to confirm that the developed product doesn’t have any bugs and working as expected.
It includes the following activities.
- Functional testing
- Non-functional testing
What is Static testing, when does it start, and what does it cover?
- It is a white box testing technique that directs the developers to verify their code with the help of a checklist to find errors in it.
- Developers can start it without actually finalizing the application or program.
- Static testing is more cost-effective than Dynamic testing.
- It covers more areas than Dynamic testing in a shorter time.
What is Dynamic testing, when does it start, and what does it cover?
- Dynamic testing involves the execution of an actual application with valid inputs and checking the expected output.
- Examples of Dynamic testing are Unit Testing, Integration Testing, System Testing, and Acceptance Testing.
- Dynamic testing happens after code deployment.
- It starts during the validation stage.
Why is White Box Testing done?
White Box Testing has many names such as Glass Box, Clear Box, and Structural Testing.
It requires the testers to gain a code-level perspective. So that, they can design cases to exploit code and find potential bugs.
Why is Black Box Testing done?
Black Box Testing is a standard software testing approach that requires testers to assess the functionality of the software as per the business requirements.
They treat the software as a black box and validate it from the end-user’s point of view.
It applies to all levels of software testing such as Unit, Integration, System, or Acceptance Testing.
What is the purpose of the Positive Testing approach?
The purpose of this testing is to ensure whether the system is confirming the software requirements or not.
Why is the Negative Testing approach used?
The purpose of this testing is to identify what the system should not do. It helps uncover potential flaws in the software.
In the next section, continue reading more general manual testing interview questions.
General Manual Testing Interview Questions Continued.
What is Test Strategy, and what does it cover?
Test strategy is an approach to carry out the testing activity.
It covers the following:
- Test Team Roles and Responsibilities
- Testing scope
- Test tools
- Test environment
- Testing schedule
- Associated risks
What is Test Plan, and what does it include?
It is the responsibility of a Test Lead or Testing Manager to create the Test Plan document.
A test plan captures all possible testing activities to guarantee a quality product. It gathers data from the product description, requirements, and use case documents.
The test plan document includes the following:
- Testing objectives
- Test scope
- Testing the frame
- The environment
- Reason for testing
- The criteria for entrance and exit
- Deliverables
- Risk factors
What is the difference between a Master Test Plan and a Test Plan?
The difference between the Master Plan and the Test Plan can be described using the following points.
1. The Master Test Plan contains all the test scenarios and risk-prone areas of the application. Whereas, the Test Plan document contains test cases corresponding to test scenarios.
2. The Master Test Plan captures every test to be run during the overall development of the application, whereas the test plan describes the scope, approach, resources, and schedule of performing the execution.
3. MTP includes test scenarios for all the phases of the application development lifecycle. Whereas, a separate test plan also exists for the Unit, Functional, and System testing, which includes cases specific to related areas.
4. A Master Test Plan suffices for big projects that require execution in all phases of testing. However, preparing a basic Test Plan is enough for small projects.
What are Test Cases?
A test case is a sequence of actions and observations that are used to verify the desired functionality.
A good test case helps to identify problems in the requirements or design of an application.
What is the difference between High-level and Low-Level test cases?
- High-level test cases cover the core functionality of a product like standard business flows.
- Low-level test cases are those related to the user interface (UI) in the application.
What is a Test Scenario?
A test Scenario represents a condition or a possibility that defines what to test.
It can have multiple test cases to cover a scenario.
How is a Test Case different from a Test Scenario?
A test case is a testing artifact to verify a particular flow with defined input values, test preconditions, expected output, and postconditions prepared to cover specific behavior.
A test scenario can have one or many associations with a test case, which means it can include multiple test cases.
What is a Test Suite?
A test suite is a group of test cases. Each test case intends to test the application functionality.
What is meant by Test Bed?
It refers to a test setup, which includes necessary H/W, S/W, N/W, AUT, and any dependency software.
What is meant by Test Environment?
Test Environment mostly refers to the essential hardware and software required to perform testing.
What is meant by Test Data?
Test data is a set of input values required to execute the test cases. Testers define the test data according to the test requirements. They can do it manually or use generation tools.
For example, if a tester is validating a graphics tool, then he would need to procure relevant data for graph generation.
What is meant by Test Harness?
A test harness is a set of scripts and demo data that tests an application under variable conditions and observes its behavior and outputs.
It emphasizes that test cases should run randomly rather than in a sequence.
What is meant by Test Coverage?
Test coverage is a quality metric to represent the amount (in %) of testing completed for a software product.
It is applicable for both functional and non-functional testing activities. This metric helps testers to add missing test cases.
Why is Code Coverage used?
Code coverage is another software engineering metric that represents the amount (in %) of code covered from unit testing.
It helps developers to add test cases for any missing functionality.
Is it possible to achieve 100% coverage of testing? How would you ensure it?
No, it’s not possible to perform 100% testing of any product. But you can follow the below steps to come closer.
- Set a hard limit on the following factors.
- Percentage of test cases passed
- The no. of bugs found
- Set a red flag if,
- Test budget depleted
- Deadlines breached
- Set a green flag if,
- The entire functionality gets covered in test cases.
- All critical & high bugs must have a status of CLOSED.
Besides the test case & test plan, what documents a tester should produce?
Here are a few other documents to prepare.
- Testing metrics
- Test design specs
- End-to-end scenarios
- Test summary reports
- Bug reports
What is a Business Requirements Document (BRD)?
BRD provides a complete business solution for a project, including the documentation of customer needs and expectations.
BRD fulfills the following objectives.
- Gain agreement with stakeholders.
- Provide clarity on the business requirements.
- Describe the solution that meets the customer/business needs.
- Determine the input for the next phase of the project.
Going ahead, you have more manual testing interview questions lined up. Check what’s in store for you next.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [Testing Types]
What is meant by Unit Testing?
Unit Testing has many names, such as Module Testing or Component Testing.
It is mostly the developers who test individual units or modules to check if they are working correctly.
What is meant by Integration Testing?
Integration Testing validates how well two or more units of software interact with each other.
There are three ways to validate integration.
- Big Bang Approach,
- Top-Down Approach,
- Bottom-Up Approach
What is the difference between a Test Driver and a Test Stub?
The test driver is a piece of code that calls a software component under test. It is useful in testing that follows the bottom-up approach.
Test stub is a dummy program that integrates with an application to complete its functionality. These are relevant for testing that uses the top-down approach.
Let’s take an example.
1. Let’s say there is a scenario to test the interface between modules A and B. We have developed only module A. Then we can check module-A if we have a real module-B or a dummy module for it. In this case, we call module-B, the Test Stub.
2. Now, module B can’t send or receive data directly from module A. In such a scenario, we’ve to move data from one module to another using some external features called Test Driver.
What is meant by the Big Bang Approach?
It means merging all the modules after testing individual modules and verifying the functionality.
It involves the use of dummy modules such as Stubs and Drivers. They make up for missing components to simulate data exchange.
Why is the Top-Down Approach used?
Testing goes from top to bottom. It first validates the High-level modules and then goes for low-level modules.
Finally, it tests the integrated modules to ensure the system is working as expected.
What is meant by the Bottom-Up Approach?
It is the reverse of the Top-Down method. In this, testing occurs from bottom to up.
It first tests the lowest-level modules and then goes for high-level modules. Finally, it verifies the integrated modules to ensure the system is working as expected.
What is meant by System Testing?
It is the last testing activity that tests the fully integrated application and confirms its compliance with business requirements.
Alternatively, we call it end-to-end testing. It verifies the whole system to ensure that the application is behaving as expected.
Can we do System testing at any stage?
No. System testing should start only if all modules are in place and work correctly. However, it should happen before the UAT (User Acceptance testing).
What are the different types of software testing?
Following is the list of various testing types used by manual testers.
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- Regression testing
- Shakeout testing
- Smoke testing
- Functional testing
- Performance testing
- Load testing
- stress testing
- Endurance testing
- White box and Black box testing
- Alpha and Beta testing
- System testing
What is meant by Smoke Testing?
Smoke testing confirms the basic functionality works for a product. It requires you to identify the most basic test cases for execution.
What is meant by Sanity Testing?
Sanity testing ensures that the product runs without any logical errors. For example, if we are testing a calculator app; we may multiply a number by three and check whether the sum of the digits of the answer is divisible by 3.
What is Exploratory Testing?
Exploratory testing is a process that lets a tester concentrate more on execution and less on planning.
- It requires formulating a test charter, a short declaration of the scope, a set of objectives, and possible approaches to be used.
- The test design and test execution activities may run in parallel without formally documenting the test conditions, test cases, or test scripts.
- Testers can use boundary value analysis to concentrate the testing effort on error-prone areas by accurately pinpointing the boundaries.
- Notes should be recorded for the Exploratory Testing sessions as it would help to create a final report of its execution.
What is Ramp Testing?
It is a testing method that proposes to raise an input signal until the system breaks down.
What is Recovery Testing?
It ensures that the program must recover from any expected or unexpected events without loss of data or functionality.
Events could be a shortage of disk space, unexpected loss of communication, or power-out conditions.
What is Reliability testing?
Reliability testing is a testing strategy to measure the consistency of Software in executing a specific operation without throwing any error for a certain period in the given environment.
Example:
The probability that a Server class application hosted on the cloud is up and running for six long months without crashing is 99.99%. We refer to this type of testing as reliability.
What is globalization testing?
Globalization testing concentrates on detecting the potential problems in the product design that could spoil globalization. It certifies that the code can handle the desired international support without breaking any functionality. And also, ensures that there would be no data loss or display problems.
What is Agile testing, and why is it important?
Agile testing is a software testing process that evaluates software from the customer’s point of view. It is beneficial because this does not require Dev to complete coding for starting QA. Instead, coding and testing both go hand in hand. However, it may require continuous customer interaction.
Why is Data Flow Testing done?
It is one of the white-box testing techniques. Data Flow Testing is done to design test cases that cover control flow paths around variable definitions and their uses in the modules. It expects them to have the following attributes:
1. The input to the module
2. The control flow path for testing
3. Pair of an appropriate variable definition and its use
4. The expected outcome of the test case
What do you know about API Testing?
API is an acronym for Application Programming Interface. It gives users access to public classes, functions, and member variables for calling them from external applications. It lays down a model for components to interact with each other.
API testing comprises three parts:
1. Data tier (database)
2. Business logic tier (PHP/J2EE)
3. Presentation tier (UI)
API testing is also a white-box testing method. It makes use of the code and a programming tool to call the API. It ignores the UI layer of the application and validates the path between the client and the API. The client software forwards a call to the API to get the specified return value. API testing examines whether the system is responding with the correct status or not.
API testing confirms the system is working from end to end. They don’t have permission to get to the source code but can use the API calls. This testing covers authorization, usability, exploratory, automated, and document validation.
What is meant by alpha testing?
Alpha testing is the initial phase of software testing where a small group of users or developers test the software product before it is released to the public. It is usually done in-house by the software development team or a select group of users who provide feedback to the developers to help them identify and fix issues before the software is released to beta testing.
Why is beta testing done?
Beta testing is a type of user acceptance testing that is conducted after the software product has completed the development and testing phase and is considered to be stable enough for release. It is usually performed by a group of end-users or customers who are invited to use the software in a real-world environment and provide feedback on its performance, usability, and overall quality.
What is meant by Gamma Testing?
Gamma testing is a type of software testing that is done after the beta testing phase and before the final release of the software product. It is also known as release candidate testing. During gamma testing, the software is tested in a production-like environment by a small group of users who were not involved in the development process. This group of users is typically made up of potential customers or end-users of the software.
The main purpose of gamma testing is to identify any remaining bugs or issues with the software product that may have been missed during the beta testing phase. The feedback from the gamma testers is used to fine-tune the software and make any necessary improvements before it is released to the general public.
How does Pilot testing differ from Beta testing?
Read the following points to know the difference between Pilot and Beta testing.
1. We do the beta test before the actual release of the product to the customer. Whereas, the pilot testing takes place in the earlier phase of the development cycle.
2. In the beta test, the testing application is given to a few users to make sure that it meets the customer requirements and does not contain any showstopper bugs. Whereas, in the pilot test, a few members of the testing team visit the customer site to set up the product. They give their feedback also to improve the quality of the end product.
What are Rainbow or Color Box Testing types?
The majority of software testers knew about the grey, black, and white box testing. Let’s see what color box tests are available.
1. White box tests
2. Black box checking
3. Grey box testing
4. Glass box tests
5. Red box scripts
6. Yellow box testing
7. Green box checking
What do you know about Structured Testing?
The other popular name for structured testing is the basis path testing. The person who invented it was Tom McCabe.
What are the steps involved in Structured Testing?
1. Derice the control flow graph from the system component.
2. Consider the cyclomatic complexity of the chart.
3. Identify a group of C basis paths.
4. Define test cases for every basis path.
5. The execution should include all the established test cases.
What does the high availability testing mean for a software tester?
High availability shows the ability of a system or a component to operate continuously without failure even at high loads for a long time.
Hence, the High availability testing confirms that a system or its sub-systems have gone through thorough checks. Also, in many cases, it simulates failures to validate whether components support redundancy or not.
What does it mean by baseline testing?
A baseline is the indicator of a specific benchmark that serves as the foundation of a new creation.
In Baseline testing, the tests capture and preserve all the results produced by the source code, and compare them against a reference baseline. This reference baseline refers to the last accepted test results. If there are new changes in the source code, then it requires a re-execution of tests to form the current baseline. If the latest results get accepted, then the current baseline becomes the reference.
What is the purpose of a failover test?
Failover testing is a test strategy to evaluate how software allocates resources and switches operations to backup systems to prevent operational failures.
What does it mean by Gorilla testing?
Gorilla Testing is a testing strategy where testers collaborate with developers as a joint force to validate a target module thoroughly from all ends.
What is the purpose of End-to-end testing?
End-to-end testing is a testing strategy to execute tests that cover every possible flow of an application from start to finish. The objective of performing end-to-end tests is to discover software dependencies and to assert that the correct input is getting passed between various software modules and sub-systems.
More manual testing interview questions on bugs, defects, and errors are available ahead.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [Bugs, Defects, Errors]
What is the primary difference between Debugging and testing?
- Testing is to find out defects while using a product, whereas debugging is to reach the part of the code, that causes failure.
- Debugging is isolating the problem area in the code done by a developer, whereas Testing is identifying the bug in an application done by a tester.
Why does software have bugs?
- Miscommunication.
- Programming errors.
- Timeline pressures.
- Change in requirements.
- Software complexity.
What are error guessing and error seeding?
Error Guessing.
It is a test case design technique in which testers have to guess the defects that might occur and write test cases to represent them.
Error Seeding.
It is the process of adding known bugs in a program for tracking the rate of detection & removal. It also helps to estimate the number of faults remaining in the program.
What will you do when a bug turns up during testing?
When a bug shows up, we can follow the below steps.
- Run more tests to make sure that the problem has a clear description.
- Run a few more tests to ensure that the same problem doesn’t exist with different inputs.
- Once we are sure of the full scope of the bug, then we can add details and report it.
Why is it impossible to test a program thoroughly?
Here are the two principal reasons that make it impossible to test a program entirely.
- Software specifications can be subjective and can lead to different interpretations.
- A software program may require too many inputs, too many outputs, and too many path combinations to test.
How do you handle a non-reproducible bug?
The following types of bugs lie under the non-reproducible category.
1. Defects observed due to low memory issue
2. Issues raised due to address pointing to a memory location that does not exist.
3. The race condition is an error scenario that occurs when the timing of one event impacts another executing in a sequence.
A tester can take the following actions to handle the non-reproducible bugs.
1. Execute test steps that are close to the error description.
2. Evaluate the test environment.
3. Examine and evaluate test execution results.
4. Keep the resources & time constraints under check.
How do you test a product if the requirements are yet to freeze?
If the requirement spec is not available for a product, then a test plan can be created based on the assumptions made about the product. But we should get all assumptions well documented in the test plan.
How will you tell if enough test cases have been created to test a product?
First of all, we’ll check if every requirement has at least one test case covered. If yes, then we can say that there are enough test cases to test the product.
If a product is in production and one of its modules gets updated, then is it necessary to retest?
It is advisable to perform regression testing and run tests for all of the other modules as well. Finally, the QA should carry out System testing.
How do we know the code has met specifications?
A traceability matrix is an intuitive tool that ensures the requirements are mapped to the test cases. When the execution of all test cases finishes with success, it indicates that the code has met the requirements.
What does the Requirement Traceability Matrix include?
A requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document that records the mapping between the high-level requirements and the test cases in the form of a table.
That’s how it ensures that the Test Plan covers all the requirements and links to their latest version.
What is GAP analysis?
Gap analysis reveals any deviation between the features available for testing and how the customer perceives them to be.
A traceability matrix is a testing tool that testers can use to track down the gaps.
What is Risk Analysis?
Risk analysis is a technique to identify the things that can go wrong in a software development project. They can negatively impact the scope, quality, timeliness, and cost of a project.
However, everyone involved in the project has a part in minimizing the risk. But it’s the leader who ensures that the whole team understands the individual role in managing the risk.
How is the Risk analysis done during software testing?
Risk analysis is the process of identifying the hidden issues that may derail the successful delivery of the application. It also prioritizes the sequence of resolving the identified risks for testing purposes.
The following are some of the risks that are of concern to the QA.
1. New Hardware
2. New Technology
3. New Automation Tool
4. The sequence of code delivery
5. Availability of test resources for the application
We prioritize them into three categories, which are as follows.
1. High importance: The impact of the bug is high on the other functionality of the application
2. Medium: It is somewhat bearable but not desirable.
3. Low: It is tolerable. This type of risk has no impact on the company’s business.
What is the difference between coupling and cohesion?
The difference between coupling and cohesion is as follows.
- Cohesion is the degree that measures the dependency of the software component that combines related functionality into a single unit, whereas coupling represents having it in a different group.
- Cohesion deals with the functionality that relates to different processes within a single module, whereas coupling deals with how much one module is dependent on the other modules within the product.
- It is good to increase the cohesion between the software, whereas coupling is discouraged.
What is CMM?
The Capability Maturity Model for Software (CMM or SW-CMM) is a model for assessing the maturity of the software processes of an organization.
It also lists down some of the standard practices that increase the maturity of these processes.
What is the Cause Effect Graph?
It is a graphical representation of inputs and the associated outputs effects which assist in designing test cases.
What do you understand of Inspection?
It’s a group-level review and quality improvement process for the product documents. It focuses on the following two aspects.
- Product document improvement
- Process improvement (of both document production and inspection)
Unlock manual testing interview questions on functional testing, let’s move to the next section to check.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [Functional Testing]
What does it mean by functional testing?
Functional testing is a software testing methodology that ensures that the application under test has all the functionality working as per the specifications provided.
What are the different types of functional testing?
Functional testing covers the following types of validation techniques.
1- Unit Testing
2- Smoke testing
3- Sanity testing
4- Integration Testing
5- Interface Testing
6- System Testing
7- Regression Testing
8- UAT
How do you conduct functional testing?
Functional testing sees the application under test as a black box. We, as a tester, first of all, write down the use cases for all the possible workflows of the said features.
After that, we verify the functionality by exercising all the said features, and their options, and ensure that they behave as expected.
What tool do you use for functional testing?
We use the Unified Functional Testing (UFT) tool developed by HP (Hewlett Packard) for both functional and regression testing.
This tool makes use of Visual Basic (VB) scripting to automate functional workflows. It allows us to integrate manual, automated, and framework-based test scripts in the same IDE.
What kind of document will you need to begin Functional testing?
- It is none other than the Functional specification document. It defines the full functionality of a product.
- Other documents are also useful in testing like the user manual and BRS.
- Gap analysis is another document that can help in understanding the expected and existing system.
What are the functional test cases?
Functional test cases are those that confirm that the application executes a specified business function. Most of these tests take the form of user or business cases that resemble standard transactions.
What are nonfunctional test cases?
Non-functional testing is done to validate the non-functional aspects (such as performance, usability, and reliability) of the application under test.
It validates the readiness of a system as given in the nonfunctional specification and never got addressed in functional testing.
What are Functional Requirements?
The functional requirements specify the behavior or function. Some of these are as follows:
- Authentication
- Business rules
- Historical Data
- Legal and Regulatory Requirements
- External Interfaces
What are the Non-Functional Requirements?
The non-functional requirements specify how the system should behave. Some of these are as follows:
- Performance
- Reliability
- Security
- Recovery
- Data Integrity
- Usability
What is the difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
In Software engineering terms, a non-functional requirement (NFR) is one that lays down the criteria for assessing the operation of a system, rather than general behavior. They often get called System Quality Attributes.
On the other hand, functional requirements are those that cover the technical aspect of the system.
Testers are bound to ask questions on SDLC and STLC. Check out the next section for manual testing interview questions on these topics.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [SDLC and STLC]
What do you know about the SDLC?
The software development life cycle is SDLC, which is a standard development framework and the foundation for processes like Waterfall, Spiral, V Models, and Agile.
It breaks down the entire development into multiple stages known as the SDLC phases like requirement collection, analysis, design, implementation/coding, testing/validation, deployment, and finally, maintenance.
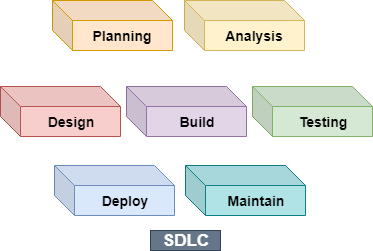
What does STLC mean?
The STLC is an acronym for the Software Testing Life Cycle. It is a testing model that proposes to execute test execution in a systematic and planned way. In the STLC model, many activities occur to improve the quality of the product.
The STLC model lays down the following steps:
1. Requirement Analysis
2. Test Planning
3. Test Case Development
4. Environment Setup
5. Test Execution
6. Test Cycle Closure
What is the Requirement Analysis phase in STLC?
The requirement analysis (RA) is the first stage of the STLC model. In this step, the testing team learns what to test & determines the testable requirements. If some specifications are not precise or have a disagreement, then the stakeholders like business analysts (BA), architects, and customers provide clarity.
What are the tasks performed in the Requirement Analysis phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the RA phase.
1. Provide a questionnaire for the customer-facing people.
2. List down the priority areas for testing.
3. Gather test environment details for carrying out the testing tasks.
4. Evaluate the possibility of test automation and prepare a report.
What is the Test Planning (TP) phase in STLC?
The second phase of STLC is test planning. It is a crucial step as the team here defines the whole testing strategy for the project.
In this stage, the test lead has to get the effort and cost estimation done for the whole project. This phase starts soon after the RA phase is over. The outcomes of the TP include the Test Planning and effort estimation documents. After the planning ends, the testing team can begin writing the test case development tasks.
What are the tasks performed in the Test Planning (TP) phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the TP phase.
1. Provide a written objective & scope for the STLC cycle.
2. Mention the testing types to cover.
3. Estimate testing efforts and resource requirements.
4. Select the testing tools required.
5. Confirm the test infra requirements.
6. List down the testing schedule and set milestones.
7. Prepare a summary of the entire testing process.
8. Create a control policy.
9. Assign roles and responsibilities.
10. Outline the testing deliverables.
11. Conclude the entry criteria, suspension/resumption criteria, and exit conditions.
12. Mark the expected risks.
What is the Test Case Development phase in STLC?
The testing team picks on the test case development tasks once the test planning (TP) phase is over. In this stage of STLC, the principal activity is to write down specific test cases for the requirements. While performing this task, they also need to prepare the input data required for testing. Once the test plan is ready, it needs to be reviewed by senior members or a team lead.
One of the documents that the team has to produce is the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM). It is an industry-wide standard for ensuring the test case gets correctly mapped with the requirement. It helps in tracking both the backward & forward direction.
What are the tasks performed in the Test Case Development phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the TCD phase.
1. Write test cases.
2. Produce scripts for automation testing (Optional).
3. Gather test data required for test execution.
What is the Test Environment Setup phase in STLC?
It is a time-consuming yet crucial activity in the STLC to prepare the test environment. Only after the test setup is available, the team can determine which conditions the application would go through testing.
It is an independent task and can go in parallel with the test case writing stage. The team or any member outside the group can also help in setting up the testing environment. In some organizations, a developer or the customer can also create or provide testing beds. Simultaneously, the test team starts writing the smoke tests to ensure the readiness of the test infra.
What are the tasks performed in the Test Environment Setup phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the TES phase.
1. Assess the need for new Software & hardware requirements.
2. Prepare the test infra.
3. Execute smoke tests and confirm the readiness of the test infra.
What is the Test Execution phase in STLC?
After the testing infra is ready, the test execution phase can start. In this stage, the team runs the test cases as per the test plan defined in the previous steps.
If a test case executes successfully, the team should mark it as Passed. If some tests have failed, then the defects should get logged, and the report should go to the developer for further analysis. As per the books, every error or failure should have a corresponding defect. It helps in tracing back the test case or the bug later.
What are the tasks performed in the Test Execution phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the TE phase.
1. Execute tests as per the test planning.
2. Provide test execution status showing the passed, failed, and skipped statistics.
3. Create defects for failed cases and assign them to the dev for resolution.
4. Perform re-execution of test cases that have defect fixes.
5. Make sure the defects get closed.
What is the Test Cycle Closure phase in STLC?
The testing team calls upon the meeting to evaluate the open defects, known issues, and code quality issues and accordingly decides on the closure of the test cycle.
They discuss what went well, and where is the need for improvement, and note the pain points faced in the current STLC. Such information is beneficial for future STLC cycles. Each member puts his/her views on the test case & bug reports and finalizes the defect distribution by type and severity.
What are the tasks performed in the Test Cycle Closure phase of STLC?
The test team performs the following tasks during the TCC phase.
1. Define closure criteria by reviewing the test coverage, code quality., the status of the business objectives, and test metrics.
3. Produce a test closure report.
4. Publish best practices used in the current STLC.
Defect metric is another popular topic amongst the interviewers. The next section covers some manual testing interview questions related to it.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [Defect Metrics]
What does a fault mean in software testing?
A fault is a condition that makes the software fail while executing the intended function.
What does an error mean in software testing?
An error represents a problem in a program that arises unexpectedly and causes it not to function correctly. An application can encounter either software errors or network errors.
What does a Failure mean in software testing?
A failure represents the incompetence of a system or component in executing the intended function as per its specification.
It could also happen in a customer environment that a particular feature didn’t work after product deployment. They would term it product failure.
What is the difference between a bug, defect, and error?
A bug is usually the same as a defect. Both of them represent an unexpected behavior of the software.
However, an error would also fall in the same category. But in some cases, errors are fixed values.
For example – 404/405 errors in HTML pages.
What is the difference between an error and a bug?
A slip in the coding indicates an Error. The error discovered by a manual tester becomes a Defect. The defect that the dev team admits is known as a Bug. If a build misses the requirements, then it is a functional failure.
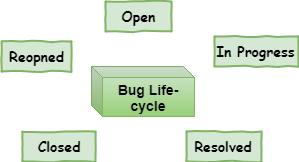
What is the Defect Life Cycle in software testing?
Defect Life Cycle also has another name, Bug Life Cycle.
The Defect Life Cycle is the representation of the different states of a defect that it attains at different levels during its lifetime. It may have variations from company to company or even get customized for some projects as the software testing process drives it to not get out of the way.
What is defect leakage?
Defect leakage, also known as “leakage” or “escape,” refers to a situation where a defect that was identified and fixed during the testing phase still manages to make its way into the production environment. In other words, the defect has “leaked” through the testing phase undetected, and has caused a problem for the end-user.
How come Severity and Priority relate to each other?
- Severity – Represents the gravity/depth of the bug.
- Priority – Specifies which bug should get fixed first.
- Severity – Describes the application point of view.
- Priority – Defines the user’s point of view.
What are the different types of Severity?
The severity of a bug can be low, medium, or high, depending on the context.
- User Interface Defect – Low
- Boundary-Related Defects – Medium
- Error Handling Defects – Medium
- Calculation Defects – High
- Misinterpreted Data – High
- Hardware Failures – High
- Compatibility Issues – High
- Control Flow Defects – High
- Load Conditions (Memory leakages under load testing) – High
What is the difference between priority and severity in software testing?
Severity represents the impact of a defect in the development or on a component in the application under test. It usually is an indication of financial loss or cost to the environment or business reputation.
On the contrary, the Priority of a defect shows the urgency of a bug yet to get a fix. For example – a bug in a server application blocked it from getting deployed on the live servers.
What does defect density mean in software testing?
Defect density is a way to measure the no. of defects found in a product during a specific test execution cycle. It is determined by dividing the defect count found by the size of the software or component.
KLOC (thousands of lines of code) is the unit used to measure the defect density.
What does the Defect Detection Percentage mean in software testing?
Defect Detection Percentage (DDP) is a type of testing metric. It indicates the effectiveness of a testing process by measuring the ratio of defects discovered before the release and reported after the release by customers.
For example – let’s say the QA logged 70 defects during the testing cycle, and the customer reported 20 more after the release. The DDP would come to 72.1% after the calculation as 70/(70 + 20) = 72.1%.
What does Defect Removal Efficiency mean in software testing?
Defect Removal Efficiency (DRP) is a type of testing metric. It is an indicator of the efficiency of the development team to fix issues before the release.
It is measured as the ratio of defects fixed to total the number of issues discovered.
For example – let’s say that there were 75 defects discovered during the test cycle, while 62 of them were fixed by the dev team at the time of measurement. The DRE would come to 82.6% after the calculation as 62/75 = 82.6%.
What does Test Case Efficiency mean in software testing?
Test Case Efficiency (TCE) is a type of testing metric. It is a clear indicator of the efficiency of the test cases getting executed in the test execution stage of the release. It helps in ensuring and measuring the quality of the test cases.
Test Case Efficiency (TCE) => (No. of defects discovered / No. of test cases executed)* 100
What is the Age of Defect in software testing?
Defect age is the time elapsed between the day the tester discovered it and the day the developer got this fixed.
While estimating the age of a defect, consider the following points.
1. The day of birth for a Defect is the day it got assigned and accepted by the dev.
2. The issues which got dropped are out of the scope.
3. The age can be both in hours or days.
4. The end time is the day got verified and closed, not just fixed by the dev.
What is Defect Clustering in software testing?
Defect clustering is a situation in testing that could arise if either most of the software bugs got discovered only in a handful of modules or the software fails to operate frequently.
What is the Pesticide Paradox in software testing?
The pesticide paradox is a situation in software testing when the same tests get repeated over and over again until they are no longer able to find new bugs.
What is the Pareto Principle in software testing?
In software testing, the Pareto Principle refers to the notion that 80% of all bugs happen to be in 20% of the program modules.
What are the different ways to apply the Pareto Principle in software testing?
Following is the list of ways to exercise the Pareto Principle in software testing:
1. Arrange the defects based on their causes, not via consequences. Don’t club bugs that yield the same outcome. Prefer to group issues depending on what module they occur in.
2. Collaborate with the dev team to discover new ways to categorize the problems. E.g., use the same static library for the components that counted for the most bugs.
3. Put more energy into locating the problem areas in the source code instead of doing a random search.
4. Re-order the test cases and pick the critical ones first to begin.
5. Pay attention to the end-user response and assess the risk areas around.
What Is Cyclomatic Complexity in Software Testing?
In software testing, the cyclomatic complexity represents a test metric known as program complexity. This method was introduced by Thomas J. McCabe in the year 1976. It sees a program as a graph using the control flow representation.
The graph includes the following attributes:
1. Nodes – A node indicates the processing tasks
2. Edges – An edge shows the control flow between the nodes.
What is the usage of Cyclomatic Complexity in software testing?
1. It gets to find the independent path for test execution.
2. It proposes that the test should cover all the branches once.
3. It gives space to concentrate on the untested paths.
4. It guarantees better code coverage.
5. It determines the risks associated with a program.
6. It aims to minimize the probable risks.
Finally, you are about to enter the last section of manual testing interview questions. It covers some of the miscellaneous questions that are worth reading.
Manual Testing Interview Questions [Miscellaneous]
What is Silk Test, and why should you use it?
Here are some facts about the Silk tool.
1. It’s a tool developed for performing the regression and functionality testing of the application.
2. It benefits when we are testing Windows-based, Java, the web, and traditional client/server applications.
3. Silk Test helps in preparing the test plan and managing it to provide direct access to the database and validation of the field.
How do you perform Automated Testing in your environment?
Automation Testing is a process of executing tests automatically. It reduces human intervention to a great extent. We use different test automation tools like QTP, Selenium, and WinRunner. These tools help in speeding up the testing tasks.
Using the above tools, we can create test scripts to verify the application automatically. After completing the test execution, these tools also generate test reports.
What are the factors that you’ll consider to choose automated testing over manual testing?
The choice of automated testing over manual testing depends on the following factors.
1. Tests require periodic execution.
2. Tests include repetitive steps.
3. Tests execute in a standard runtime environment.
4. Automation is expected to take less time.
5. Automation is increasing reusability.
6. Automation reports are available for every execution.
7. Small releases like service packs which include a minor bug fix. In such cases, executing the regression tests is sufficient for validation.
What are the essential qualities of an experienced QA or Test Lead?
Every QA or Test Lead should have the following qualities.
1. Well-versed in software testing processes.
2. Ability to accelerate teamwork to increase productivity.
3. Improve coordination between QA and Dev engineers.
4. Provide ideas to refine the QA processes.
5. Ability to conduct RCA meetings and draw conclusions.
6. Excellent written and interpersonal communication skills.
7. Quick learner and able to groom team members.
Summary – Manual Testing Interview Questions
We always try that our study material helps you the most in your work. That’s why we came up with this blog post on the top manual testing interview questions for both beginner and experienced test engineers.
We hope you get to read the right questions and answers that you need. If you would have enjoyed reading, then follow us on our social media accounts for updates.
Keep Learning,
TechBeamers