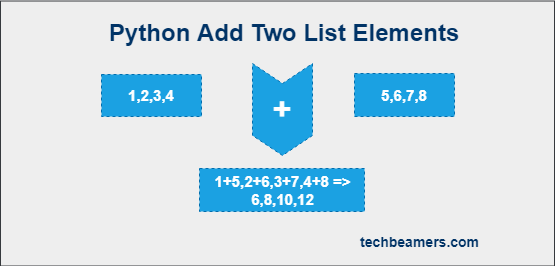
This tutorial describes four unique ways to add elements of two lists in Python. For example – using a for loop to iterate the lists, add corresponding elements, and store their sum at the same index in a new list. Some of the other methods you can use are using map() and zip() methods.
All of these procedures use built-in functions in Python. However, while using the map(), you’ll require the add() method, and zip() will need to be used with the sum() function. Both these routines are defined in the operator module, so you would have to import them into your program. After finishing up this post, you can assess which of these ways is more suitable for your scenario.
By the way, it will be useful if you have some elementary knowledge about the Python list. If not, please go through the linked tutorial.
Python Add Two List Elements – 4 Unique Ways
For loop to add elements of two lists
It is the simplest approach to add elements of two lists. In this method, Python for loop is used to iterate the smaller of the two lists. In every iteration, add the corresponding values at the running index from the two lists, and insert the sum in a new list.
# Python add two list elements using for loop
# Setting up lists
in_list1 = [11, 21, 34, 12, 31, 26]
in_list2 = [23, 25, 54, 24, 20]
# Display input lists
print ("\nTest Input: **********\n Input List (1) : " + str(in_list1))
print (" Input List (2) : " + str(in_list2))
# Using for loop
# Add corresponding elements of two lists
final_list = []
# Choose the smaller list to iterate
list_to_iterate = len(in_list1) < len(in_list2) and in_list1 or in_list2
for i in range(0, len(list_to_iterate)):
final_list.append(in_list1[i] + in_list2[i])
# printing resultant list
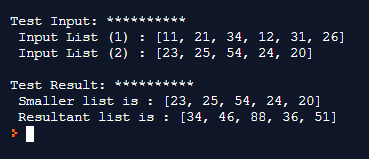
print ("\nTest Result: **********\n Smaller list is : " + str(list_to_iterate))
print (" Resultant list is : " + str(final_list))You can see the addition of elements of two lists in Python from the below example.
List comprehension to add elements of two lists
Python list comprehension is a unique shorthand technique in Python to create lists at runtime. It lets the programmer perform any operation on the input list elements.
This method is also a bit faster for manipulating the list data structure. Check out the below sample Python program.
# Python add two list elements using list comprehension
# Setting up lists
in_list1 = [11, 21, 34, 12, 31]
in_list2 = [23, 25, 54, 24, 20, 27]
# Display input lists
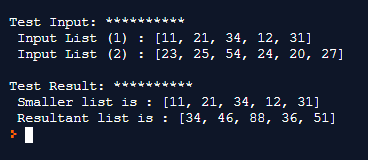
print ("\nTest Input: **********\n Input List (1) : " + str(in_list1))
print (" Input List (2) : " + str(in_list2))
# Using list comprehension
# Add corresponding elements of two lists
final_list = []
# Choose the smaller list to iterate
list_to_iterate = len(in_list1) < len(in_list2) and in_list1 or in_list2
final_list = [in_list1[i] + in_list2[i] for i in range(len(list_to_iterate))]
# printing resultant list
print ("\nTest Result: **********\n Smaller list is : " + str(list_to_iterate))
print (" Resultant list is : " + str(final_list))This program will produce the following result:
map() and add() functions to add given lists
Python map() is one of the higher-order functions in Python. It takes another method as its first argument, along with the two lists.
Both the input lists are passed to the input function (add() in our case) as parameters. This function adds up the elements of two lists and returns a Python iterable as output.
We convert the iterable into a list using the list constructor method. Check out the complete example below:
# Python add two list elements using map() and add()
from operator import add
# Setting up lists
in_list1 = [11, 21, 34, 12, 31]
in_list2 = [23, 25, 54, 24, 20, 27]
# Display input lists
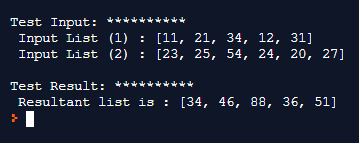
print ("\nTest Input: **********\n Input List (1) : " + str(in_list1))
print (" Input List (2) : " + str(in_list2))
# Using map() and add()
# Add corresponding elements of two lists
final_list = list(map(add, in_list1, in_list2))
# printing resultant list
print ("\nTest Result: **********\n Resultant list is : " + str(final_list))This example will give the following outcome:
zip() and sum() functions to add given lists
The sum() function adds list elements one by one using the index. And Python zip() function groups the two list items together.
This approach is also an elegant way to add elements of two lists in Python. Check out the full example with the source code below:
# Python add two list elements using zip() and sum()
# Setting up lists
in_list1 = [11, 21, 34, 12, 31, 77]
in_list2 = [23, 25, 54, 24, 20]
# Display input lists
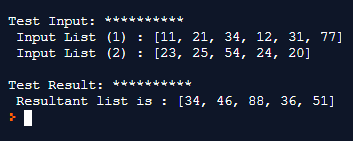
print ("\nTest Input: **********\n Input List (1) : " + str(in_list1))
print (" Input List (2) : " + str(in_list2))
# Using zip() and sum()
# Add corresponding elements of two lists
final_list = [sum(i) for i in zip(in_list1, in_list2)]
# printing resultant list
print ("\nTest Result: **********\n Resultant list is : " + str(final_list))The above code will provide the following output:
You’ve seen various methods here for Python Add two list elements. Now, you can choose any of them based on your business case. By the way, to learn Python from scratch to depth, do read our step-by-step Python tutorial.