This tutorial intends to train you on using Python Heapq (An Implementation of Heap Queue). It is a module in Python that uses the binary heap data structure and implements Heap Queue a.k.a. Priority Queue algorithm.
How to Use Heapq in Python?
Interestingly, the Heapq module uses a regular Python list to create a Heap. It supports the addition and removal of the smallest element in O(log n) time. Hence, it is an obvious choice for implementing priority queues.
The Heapq module includes seven functions, the first four of which are used for heap operations. However, you need to provide a list as the heap object itself.
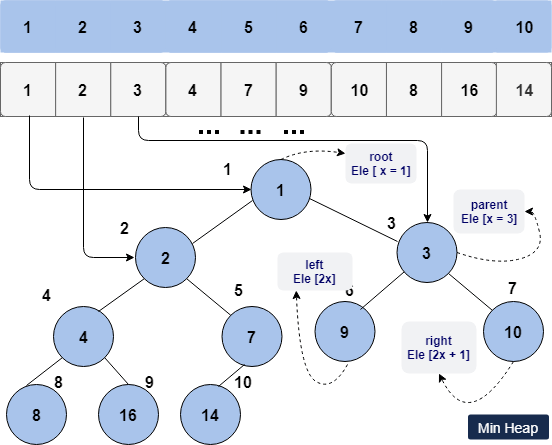
The heap data structure has a property that it always pops out the smallest of its elements (Min Heap). Also, it keeps the heap structure intact despite any push or pop operation. The heap[0] would also point to the smallest value of the Heap.

Let’s now look at this topic in detail by answering some of your general questions first.
What is a Priority Queue?
Priority Queue is an advanced data type (ADT) which is a more refined version of a Queue. It dequeues higher-priority items before the lower-priority items. Most programming languages such as Python use Binary heap to implement it.
Python Heapq, as stated in the beginning, provides a min-heap implementation.
What is a Heap?
A heap has multiple meanings in computer science. Sometimes, it refers to a memory area in a program used for dynamic allocation. However, in this tutorial, we are talking about the Heap Data Structure, which is a complete binary tree. It helps in implementing priority queues (PQ), the heapsort, and some graph-based algorithms.
A heap has the following two variants:
- A max-heap, in which the parent is more than or equal to both of its child nodes.
- A min-heap, in which the parent is smaller or equal to the child nodes.
Below is a general representation of a binary heap.
What does the Heapq Module Provide?
Heapq is a Python module that provides an implementation of the Min heap. It makes use of a Binary heap and exposes several functions to implement a priority queue.
You may eventually solve many programming problems using its functions. For example, find the two largest numbers from a list of integers in Python.
There happen to be many ways to address this problem. However, none is as intuitive and faster than a Heapq solution.
Out of many Python Heapq functions, one is nlargest(). It returns a list-type object containing the desired number of largest elements. Below is a short example before we dig into the more complicated ones.
Also Read: Python Array Explained with Examples
Python Heapq Example
# A brief heapq example
# Find the two largest integers from a list of numbers
import heapq as hq
list_of_integers = [21, 67, 33, 13, 40, 89, 71, 19]
# Find two largest values
largest_nums = hq.nlargest(2, list_of_integers)
print("Two largest numbers are: ", largest_nums)The output is:
Two largest numbers are: [89, 71]
Please note that you can create a heap in either of these two ways:
- Initialize the list with [].
- Pass a pre-filled list into
heapify()to convert to a heap.
Let’s now check out what functions this module provides.
Python Heapq Functions
The Heapq module has the following methods:
1. heappush()
It adds an element to the heap. Don’t apply it on any old list, instead use the one that you built using Heap functions. That is how you can ensure the elements are in the desired order.
# heappush() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.heappush(heap, element)
Check out the below Heapq heappush() example.
# A brief heapq.heappush() example
import heapq as hq
import random as r
init_list = list(range(10, 99, 10))
print("Step-1: Seed data for the heap: ", init_list)
r.shuffle(init_list)
print("Step-2: Randomize the seed data: ", init_list)
# Creating heap from an empty list
heap = []
print("Step-3: Creating heap...")
# Demonstrating heapq.heappush() function
[hq.heappush(heap, x) for x in init_list]
# Printing heap content to see if the smallest item is at 0th index
print(" a. Heap contains: ", heap)
# Adding another smaller item to the heap
hq.heappush(heap, 1)
print(" b. Heap contains: ", heap)This code results in the following:
Step-1: Seed data for the heap: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90] Step-2: Randomize the seed data: [70, 20, 60, 80, 90, 30, 40, 10, 50] Step-3: Creating heap... a. Heap contains: [10, 20, 30, 50, 90, 60, 40, 80, 70] b. Heap contains: [1, 10, 30, 50, 20, 60, 40, 80, 70, 90]
You can observe that the heap kept the smallest item at the 0th index. We added a new lower value using the heappush() function. And, it pushed that to the 0th position by shifting the previous value to the 1st index.
2. heappop()
It is used to remove the smallest item that stays at index 0. Moreover, it also ensures that the next lowest replaces this position:
# heappop() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.heappop(heap)
Check out the Heapq heappop() example. You need to append this code to the previous heappush() example.
# Exercising heapq.heappop() function
print("Step-4: Removing items from heap...")
out = hq.heappop(heap)
print(" a. heappop() removed {} from heap{}".format(out, heap))
out = hq.heappop(heap)
print(" b. heappop() removed {} from heap{}".format(out, heap))
out = hq.heappop(heap)
print(" c. heappop() removed {} from heap{}".format(out, heap))It will give the following result:
Step-4: Removing items from heap... a. heappop() removed 1 from heap[10, 20, 40, 50, 30, 70, 80, 90, 60] b. heappop() removed 10 from heap[20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90] c. heappop() removed 20 from heap[30, 50, 40, 90, 60, 70, 80]
It is clear from the output that heappop() always pops off the lowest element from the heap.
3. heappushpop()
This function first adds the given item to a Heap, then removes the smallest one and returns it. So, it is an increment of both heappush() and heappop(). But it tends to be a little faster than the two combined.
# heappushpop() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.heappushpop(heap, element)
Check out the Heapq heappushpop() example. You need to append it to the previous code sample.
# Exercising heapq.heappushpop() function
print("Step-5: Adding & removing items from heap...")
new_item = 99
out = hq.heappushpop(heap, new_item)
print(" a. heappushpop() added {} and removed {} from heap{}".format(new_item, out, heap))
new_item = 999
out = hq.heappushpop(heap, new_item)
print(" b. heappushpop() added {} and removed {} from heap{}".format(new_item, out, heap))The output is:
Step-5: Adding & removing items from heap... a. heappushpop() added 99 and removed 30 from heap[40, 60, 50, 70, 90, 99, 80] b. heappushpop() added 999 and removed 40 from heap[50, 60, 80, 70, 90, 99, 999]
4. heapify()
This function accepts an arbitrary list and converts it to a heap.
# heapify() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.heapify(heap)
Here is how we can use the heapify()function.
# A brief heapq.heapify() example
import heapq as hq
heap = [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99]
print("Raw heap: ", heap)
hq.heapify(heap)
print("heapify(heap): ", heap)After running the above code, we get the following result:
Raw heap: [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99] heapify(heap): [11, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99]
You can see that the heapify() function transformed the input list and made it a heap.
5. heapreplace()
It deletes the smallest element from the Heap and then inserts a new item. This function is more efficient than calling heappop() and heappush().
# heapreplace() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.heapreplace(heap, element)
Have a look at the below Heapq heapreplace() example.
# A brief heapq.heapreplace() example
import heapq as hq
heap = [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99]
hq.heapify(heap)
print("heap: ", heap)
hq.heapreplace(heap, 12)
print("heapreplace(heap, 12): ", heap)
hq.heapreplace(heap, 100)
print("heapreplace(heap, 100): ", heap)The output is:
heap: [11, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99] heapreplace(heap, 12): [12, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99] heapreplace(heap, 100): [13, 34, 78, 78, 45, 100, 99]
6. nlargest()
This function returns the n largest elements from a given iterable. It also accepts a key which is a function of one argument.
The selected items have to satisfy the k function. If any of them fails, then the next higher number is considered.
# nlargest() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.nlargest(n, iterable, key=None)
Let’s see how the Heapq nlargest() function works. We called it to get the two largest numbers.
# heapq.nlargest() example without a key
import heapq as hq
heap = [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99]
hq.heapify(heap)
print("heap: ", heap)
out = hq.nlargest(2, heap)
print("nlargest(heap, 2): ", out)The result is:
heap: [11, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99] nlargest(heap, 2): [99, 78]
Check out another Heapq nlargest() example. It not only requests for the two largest numbers but also has a is_even() function as the KEY.
If any of the selected numbers fail to clear the KEY function, then the next one comes in.
# heapq.nlargest() example with key
import heapq as hq
def is_even(num):
if num%2 == 0: return 1
return 0
heap = [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99]
hq.heapify(heap)
print("heap: ", heap)
out = hq.nlargest(2, heap, is_even)
print("nlargest(heap, 2): ", out)The output is:
heap: [11, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99] nlargest(heap, 2): [34, 78]
7. nsmallest()
It is also similar to the nlargest() in operation. However, it gets the n smallest elements from a given iterable. It too accepts a key which is a function of one argument.
The selected items have to satisfy the k function. If any of them fails, then the next smaller number is considered.
# nsmallest() Syntax import heapq as hq hq.nsmallest(n, iterable, key=None)
Here is a simple example of using the Heapq nsmallest() function. We called it to fetch the two smallest numbers.
# heapq.nsmallest() example
import heapq as hq
heap = [78, 34, 78, 11, 45, 13, 99]
hq.heapify(heap)
print("heap: ", heap)
out = hq.nsmallest(2, heap)
print("nsmallest(heap, 2): ", out)Here is the result:
heap: [11, 34, 13, 78, 45, 78, 99] nsmallest(heap, 2): [11, 13]
You can achieve similar behavior in other ways, but the heap algorithm is more memory-efficient and even faster.
Checkout: Python Exercises for Beginners
Python Heapq Exercises
Now, have some exercises where you can practically use the Heapq.
First Exercise
Write a Python program to push elements and pop off the smallest one.
import heapq as hq
heap = []
hq.heappush(heap, ('H', 9))
hq.heappush(heap, ('H', 7))
hq.heappush(heap, ('H', 4))
hq.heappush(heap, ('H', 1))
print("Elements in the heap:")
for ele in heap:
print(ele)
print("----------------------")
print("Calling heappushpop() to push element on the heap and return the smallest one.")
hq.heappushpop(heap, ('H', 11))
for ele in heap:
print(ele)The output:
Elements in the heap:
('H', 1)
('H', 4)
('H', 7)
('H', 9)
----------------------
Calling heappushpop() to push element on the heap and return the smallest one.
('H', 4)
('H', 9)
('H', 7)
('H', 11)Second Exercise
Write a Python program to perform Heap Sort, push all items to a heap, and then take off the smallest ones one after the other.
import heapq as hq
def heap_sort(heap):
in_list = []
for value in heap:
hq.heappush(in_list, value)
return [hq.heappop(in_list) for i in range(len(in_list))]
out = heap_sort([9, 7, 5, 2, 1, 2, 8, 10, 6, 5, 4])
print(out)Here is the result:
[1, 2, 2, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
More Exercises for Practice
There are many other problems that you may like to solve. Some of these are as follows:
3. Where will you find the third smallest key in a heap?
Ans. We can get the third-smallest key from:
- The nodes with a depth level of 1 or 2
4. Where will you get the largest key in a heap?
Ans. The largest key is most likely to be stored at an external/leaf node (without children)
5. Describe a sequence of n insertions in a heap that takes Ω(nlogn) time to complete.
Summary – Using Python Heapq Module
With the Heapq module, you can implement several kinds of priority queues and schedulers. It has vast usage in different areas such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning, Operating systems (OS), and graphs.
Anyway, after wrapping up this tutorial, you should feel comfortable using Python Heapq. However, you may practice more with examples to gain confidence.
Also, to learn Python from scratch to depth, read our step-by-step Python tutorial.