In this Python programming class, we’ll explain the concept of the Python module, its purpose, and syntax, and demonstrate with examples. Please note that modules are the pillars of modular programming in Python.
Modules in Python
Greetings readers, in this tutorial, you will learn about modules in Python and their usage. We are also going to teach you how to implement them in Python.
Note: We are going to teach according to Python 3 syntax. With slight modification, you can use the code snippets on Python 2.
1. Introduction to Python Module
Modules are primarily the (.py) files that contain Python code defining functions, classes, variables, etc. with a suffix .py appended in its file name.
They can have different functions, variables, and classes in one file. We can also call them libraries.
A Python module brings certain benefits such as we can reduce redundancy in the code. It can let us maintain uniformity in the coding style.
Example: Take a file called math_function_def.py
It could contain functions for calculating the factorial value of a number, cube, square root, constant values such as the value of pi, Fibonacci sequence generation code, etc.
Generally, it is a good practice to create modules that have a fixed purpose. It increases readability and increases productivity and bug reporting.
A few examples of modules are:
From Python Standard Library:
- OS, Time, Math, MatPlotlib, etc.
From Online Sources:
- Keras(for deep learning), Numpy(for number manipulation), Pandas(for array manipulation), etc.
2. Python Module: Mechanism
2.1. Mechanism
For systems where Python is pre-installed or when installed using the system package manager such as apt-get, dnf, zypper, or using package environment managers like Anaconda the following applies.
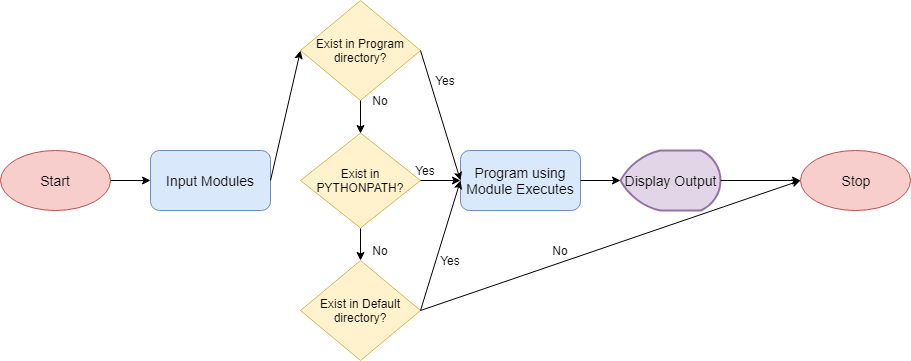
When we import modules, the Python interpreter locates them in three locations:
- The directory from the program is executed
- The directory specified in the PYTHONPATH variable (A shell variable or an environment variable)
- The default directory (It depends on the OS distribution.)
The Flowchart for the above mechanism is as follows:
2.2. Modules Listing
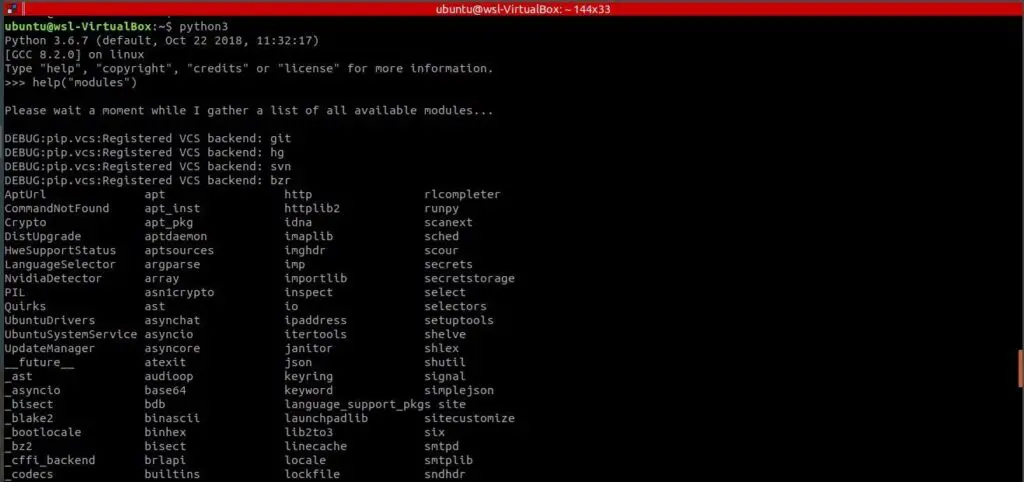
To find out the list of modules present in Python, we can issue the command: help(“modules”) in the Python interpreter shell.
Executing the above command will return the list of available modules, as shown below:
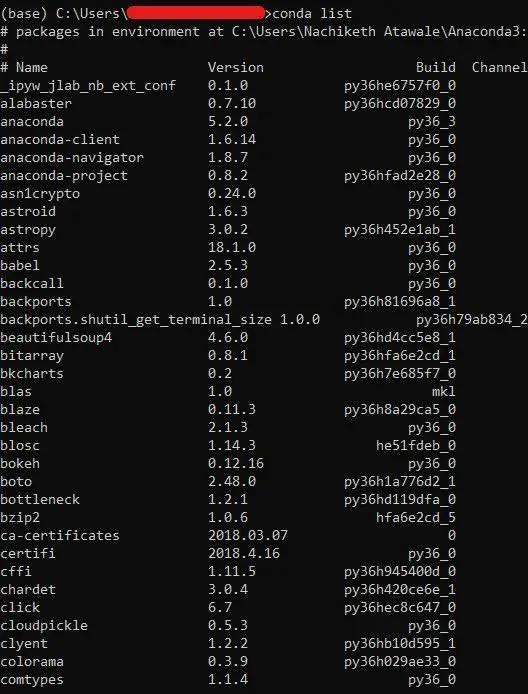
Besides, you can also issue the pip list or conda list command in the console to list all available modules.
The following diagram shows the output for the second method in Windows 10 cmd shell.
3. Modules: Implementation
3.1. Importing of Modules from Standard Python Path
Syntax – Using Full Name
import module_name1, module_name2…
Example:
import os
If the module name is too long to type, we can assign an alias as short as a single letter.
Syntax – Using a Short Name
import module_name as shortened_module_name
Example:
import math as m
It is a time-saver for those who have module names that are too long to remember to type.
3.2. Importing Modules from New Sources
To load new modules from new Sources, we must install using Python pip a software utility that installs Python modules from the Python index online or using a package environment manager like Anaconda.
Python PIP to Install New Modules
Run the following command to install a Python module.
python -m pip3 install module_package_name
Anaconda to Install new Modules
Run the following command to install a Python module
conda install module_package_name
System Package Manager to Install New Modules
Run the following command to install a Python module on Ubuntu.
sudo apt install module_package_name
For example, If we want to install Numpy.
python -m pip3 install numpy conda install numpy sudo apt install python3-numpy
4. Module Program Examples
4.1. Built-In Modules
There are several built-in modules such as dir(), math(), random(), time(), datetime() etc.
Example Program:
import math, random #we can write multiple modules in one import statement. print (math.sqrt(625)) #prints square root of number 625 print (math.factorial(10)) #prints factorial value of a number 10 print (math.pi) #prints value of pi according to the built-in module print (random.randint(1,20)) #prints a random value from integers 1-20 print (dir(math)) #prints function name, variables,etc in math module
4.2. User-Defined Python Module
Take a Python file, for example, factorial_definition.py
def get_factorial(param):
out = 1
if param < 0:
print("Factorial not allowed for -ve numbers")
out = None
elif param == 0:
print("Factorial(0) = 1")
out = None
else:
for i in range(1, param + 1):
out = out*i
return out
# For testing purpose:
# in_value = -1
# in_value = 0
# in_value = 5
# out = get_factorial(in_value)
# if out != None:
# print(f"Factorial of {in_value} is {out}")Save this file either in PYTHONPATH or in the path where another program resides which will import the module.
To import this file, we use the following code in the program, which will load the module.
import factorial_definition factorial_definition.factorial()
We can call the variable Pi using factorial_definition.Pi
Since the module name is long, we can rename it in the manner import factorial_definition as fact and use this to call the variables and variables.
If we want we can import only the Pi variable, to do so, we use from factorial_definition import Pi.
5. Usages of Modules
Modules are used to reduce the redundant statements in a program. It saves time and increases readability as well as productivity. They are also used to extend the functionality of Python and allow different developers around the world to work in a coordinated manner.
For example, Google developed Tensorflow, which contains functions for deep learning and is open for contributions from the past many years. It is an open-source module so that various people from different parts of the world can participate and improve the scope of deep learning applications.
The TensorFlow library uses the icon shown below.

Other examples of open-source modules are Keras, OpenCV, etc.
Keras Module

OpenCV Module
To Learn more topics, read the latest Python tutorial.
Conclusion
This tutorial has provided a comprehensive overview of Python modules, including what they are, how to create them, and how to use them. Python modules are a powerful way to organize and reuse code. By grouping related functions and classes into modules, you can make your code more modular and easier to maintain.
Before we leave, let’s share some tips for using Python modules effectively:
- Use descriptive names for your modules and functions. This will make it easier to understand and use your code.
- Document your modules and functions. This will help other people understand how to use your code.
- Import only the modules and functions that you need. This will help to keep your code efficient.
- Use namespaces to avoid name collisions. This can happen when you import multiple modules that have functions with the same name.