This tutorial describes Java access modifiers in detail. They control the visibility of Java classes and their members (functions and data). They are public, private, and protected.
Understand Java Access Modifiers with Examples
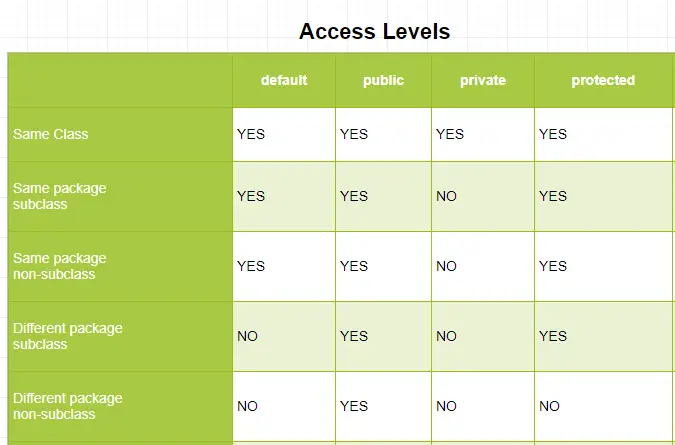
However, Java also implements a default case when no modifier is present. It means that a class, its functions, and fields are only accessible by other classes in the same module.
By the way, there are four types of access modifiers in Java. Let’s discuss each of them in detail and with the help of examples.
The following are the points that we’ll discuss today.
Introduction to Java access modifiers
Java provides a wide variety of mechanisms to control the visibility of objects of a class or variable. They are known as modifiers in programming terminology.
As a matter of fact, they belong to one of the following categories:
- Access modifiers
- Non-Access modifiers
Moreover, Java supports four primary access modifiers. While Non-access specifiers are of 7 types in Java. You can use them to specify the level of access to classes, methods, constructors, or variables.
Firstly, we’ll cover the four primary access specifiers which are as follows:
- Default access modifier
- Private access modifier
- Public access modifier
- Private access modifier
As per the Java inheritance concept:
- The public methods of a superclass must also have the same level in the subclass.
- Private methods wouldn’t be available to child classes.
- Protected methods in the superclass are either public or protected in a subclass.
Default access modifiers
The default access modifier is accessible to any package by default. The programmers need not specify any keyword to use the default access modifier.
It means that the programmer doesn’t need to specify a class, method, or constructor default explicitly.
A class or method is, by default, accessible from any other “class” that exists in the same package. We usually don’t define variables and methods with any access modifier.
Given these points, here is an example illustrating the default class:
class Def {
int num = 175;
void print() {
System.out.println("Default class " + num);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Def def = new Def();
def.print();
}
}As you would expect, the output is:
Default class 175
Private access modifiers
As the name suggests, the private access modifier limits access to the defining “class” only. With the help of the “private” keyword, we can implement the real concept of Data Encapsulation. It means to hide the private members from the outside world.
Also, please note that all user-defined variables, constructors, or methods can also have private access. Check out the following points:
- The functions labeled as private are accessible within the class only.
- You can’t declare a top-level class or interface in Java as private. And, even if you do, it would be useless as no one could access it.
- The programmer must define a getter or setter to access private methods or variables.
Given these points, consider the below example to visualize the use of private access modifiers:
class Priv {
private void PRINT() {
System.out.println("PRINT(): Private access");
}
public void getPrint() {
System.out.println("getPrint(): Calling PRINT()");
PRINT();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Priv priv = new Priv();
System.out.println("Private access");
priv.PRINT();
priv.getPrint();
}
}In this example, the getPrint() is a getter function for the private function PRINT(). The output is:
Test.java:16: error: PRINT() has private access in Priv
In order to fix the above error, comment the priv.PRINT(); line and then run the above program:
Private access getPrint(): Calling PRINT() PRINT(): Private access
Public access modifiers
The public modifiers are the most common in Java applications. They mean that any public class, method, variable, interface, or constructor is accessible throughout the package.
- Before using a public class in another package, you must first import it.
- If you inherit a public class, then the subclass will have all its methods and variables by default.
For your info, the “main()” method in Java is public.
class First {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
public class Main extends First {
public static void main(String args[]) {
First first = new First();
first.print();
}
}The output is:
Hello
Protected access modifiers
Objects or methods having protected access are visible to the package and subclasses only.
The following are a few points to elaborate on the exact behavior:
- These methods, variables, or constructors are accessible within the package only and also available to all the subclasses.
- The protected keyword doesn’t apply to any class or interface.
- Interface methods or variables can’t have protected access.
Look at an example below:
class First {
protected static int count;
public void update(){
System.out.println(++count);
}
}
public class Main extends First {
public static void main(String args[]) {
First out = new First();
out.update();
}
}The output is:
1
Non-access modifiers
In Java programming, you will get seven non-access modifiers. You may prepend them with classes/methods/variables/constructors and use them in programs.
Here are some points to help you understand when should you use a particular modifier.
- Static – It means something is directly related to a class.
- Final – It indicates that the object is immutable.
- Abstract – It means you need to subclass for creating objects.
- Synchronized – It indicates that only one thread can execute a method at a time.
- Transient – It means to exclude something during serialization.
- Volatile – It indicates that different threads can modify a variable’s value.
- Native – It shows that the method is available in the native code using JNI or JNA.
Key points
Here is a quick summary of the above concepts. It’ll help you make better use of access modifiers in Java.
- If you are writing a class for reuse, then apply the most restrictive access level to those fields where it is logical.
- Also, make private access your default choice until there is a solid contrary case.
- Moreover, don’t ever label constant identifiers as public.
We hope that reading this tutorial has added a bit to your knowledge stack. If you wish to learn more, then please refer to the below post for the next steps.








