Hello friends, you can use three common ways to format strings in Java. This tutorial explains these methods: String’s format(), printf, and StringBuilder. It includes examples to demonstrate their usage and discuss the parameters, return types, and potential errors.
Understand Different Ways to Format Strings in Java
String formatting in Java is primarily achieved using the String.format() method, which is similar to C’s printf function. It allows you to create formatted strings with placeholders for variables, making it easier to build complex output. Let’s dive into the different formatting options.
Basic String Formatting in Java
The most common choice to format strings in Java is to use the String class format() method. With this method, you can dynamically place another string, a number either integers or floats. Check the function syntax below:
Java String Format Syntax
| Signature | Description |
|---|---|
SyntaxString.format(String format, Object... args) | Returns a formatted string using the specified format and arguments. |
Argumentsformat (String):args (Object…): | The format string with placeholders. One or more objects to replace the placeholders. |
| Return Value | Returns a formatted string. |
| Potential Exceptions | IllegalFormatException if the format string is illegal or incompatible with the arguments. |
Basic String Format Examples
It is the most basic formatting shown in the below example.
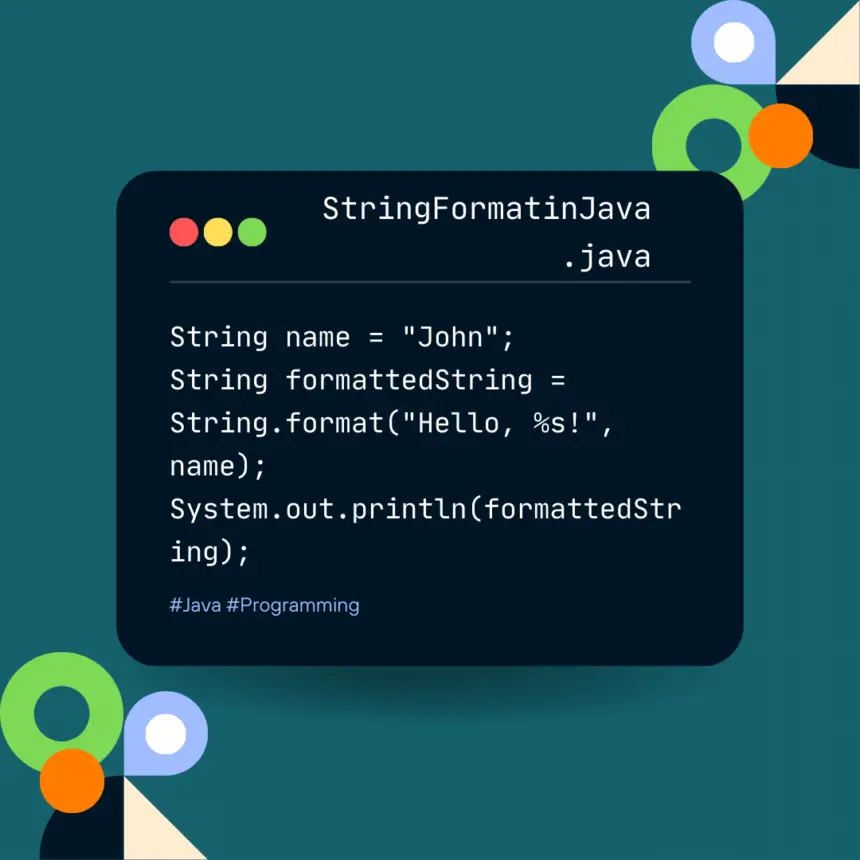
public class BasicStringFormattingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "John";
String formattedString = String.format("Hello, %s!", name);
System.out.println(formattedString);
}
}This code will print: “Hello, John!”
In this example, the string is getting filled with integer numbers at runtime.
public class IntegerFormattingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 30;
String formattedString = String.format("I am %d years old.", age);
System.out.println(formattedString);
}
}This code will print: “I am 30 years old.”
This example is formatting a string with floating-point numbers.
public class FloatingPointFormattingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double price = 29.99;
String formattedString = String.format("The price is $%.2f", price);
System.out.println(formattedString);
}
}This code will print: “The price is $29.99.”
Using Different String Format Specifiers
In Java, you can control the width, precision, and alignment of the formatted string by using additional specifiers. These specifiers are part of the format string.
%10s: Right-align a string within a 10-character-wide field.%-10s: Left-align a string within a 10-character-wide field.%5.2f: Format a floating-point number with a total width of 5 characters and 2 decimal places.
The below example shows how to use the specifiers with the Java string format method.
Runnable Code:
public class FormattingSpecifiersExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String city = "New York";
int population = 8375000;
double area = 468.48;
String formattedString = String.format("%-15s | %10d | %8.2f", city, population, area);
System.out.println(formattedString);
}
}This code will format and print data in a table-like manner:
New York | 8375000 | 468.48Format Date-Time String in Java
Java provides a separate class, SimpleDateFormat, for formatting date-time. However, we’ll discuss it separately. Here, let’s format a date-time string using the %t.
In the %t specifier, there is no direct use of “F” or “T” as standalone format flags. The correct way to use the %t specifier is in combination with other format flags to format dates and times in Java. Let’s clarify:
- %t: The
%tspecifier itself is a placeholder that is used in conjunction with other format flags to format various date-time components. It doesn’t have a specific meaning on its own; it serves as a prefix for other format flags.
Using %t for Date-Time Formatting
When you use %t along with other format flags, you can format date-time components. For example:
| %t Specifier | Short Description |
|---|---|
%tF | Formats the full date as “YYYY-MM-DD” (e.g., “2023-10-12”). |
%tT | Formats the full-time as “HH:MM: SS” (e.g., “12:34:56”). |
%tY | Formats the year with century as a base-10 number (e.g., “2023”). |
%tm | Formats the month as a base-10 number (01-12) (e.g., “10” for October). |
%td | Formats the day of the month as a base-10 number (01-31) (e.g., “12”). |
%tH | Formats the hour of the day as a base-10 number (00-23) (e.g., “12” for 12 o’clock). |
%tM | Formats the minute as a base-10 number (00-59) (e.g., “34” for 34 minutes past the hour). |
%tS | To format the second as a base-10 number (00-60) (e.g., “56” for 56 seconds). |
Java Date-Time Formatting Example
So, when you see %tF, it combines the date components to format the date in the “YYYY-MM-DD” pattern. Whereas, %tT combines the time components to format the time in the “HH:MM: SS” pattern. These format flags work in combination with %t displaying the desired output format for date-time components in Java.
Check out the below Java code exercising different options to format date-time values.
Runnable Code:
import java.util.Date;
public class DateTimeFormatExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Date object representing the current date & time
Date currentDate = new Date();
// Format and display date & time components
String fullDate = String.format("Full Date: %tF", currentDate); // YYYY-MM-DD
String fullTime = String.format("Full Time: %tT", currentDate); // HH:MM:SS
String year = String.format("Year: %tY", currentDate); // YYYY
String month = String.format("Month: %tm", currentDate); // MM
String day = String.format("Day: %td", currentDate); // DD
String hour = String.format("Hour: %tH", currentDate); // HH (00-23)
String minute = String.format("Minute: %tM", currentDate); // MM (00-59)
String second = String.format("Second: %tS", currentDate); // SS (00-60)
// Display formatted date & time components
System.out.println(fullDate);
System.out.println(fullTime);
System.out.println(year);
System.out.println(month);
System.out.println(day);
System.out.println(hour);
System.out.println(minute);
System.out.println(second);
}
}In this code, we create a Date object representing the current date & time and use String’s format() to format and store various date & time components as strings. We then use System.out.println() to display the formatted date & time components as specified in the comments.
Advanced String Formatting
You will be happy to learn that Java provides some special ways to handle complex string formatting. Below are the step-by-step details on how to use these methods.
Using printf for Stream Output
The System.out stream provides a convenient way to format and print data using the printf method.
| Item name | Description |
|---|---|
Method DescriptionPrintStream.printf(String format, Object... args) | Formats and prints a formatted string to the output stream. |
Argumentsformat (String)args (Object…) | The format string with placeholders and specifiers. One or more objects to replace the placeholders and specifiers. |
| Return Value | None (void). |
| Potential Exceptions | No checked exceptions, however, exceptions like FormatMismatchException, MissingFormatArgumentException, and IllegalFormatException may occur due to mismatches between format specifiers. |
Runnable Code:
public class PrintfStreamOutputExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String item = "Laptop";
int quantity = 3;
double itemPrice = 899.99;
System.out.printf("Item: %s, Quantity: %d, Price: $%.2f%n", item, quantity, itemPrice);
}
}This code will format and print the item details, like “Item: Laptop, Quantity: 3, Price: $899.99.”
Using StringBuilder for Complex Formatting
For more complex formatting, you can use StringBuilder. It is more efficient when you need to concatenate multiple strings and format them.
| Item name | Description |
|---|---|
Method DescriptionStringBuilder | A class for building strings with efficient concatenation. |
| Arguments | None |
| Return Value | A StringBuilder object. |
| Potential Exceptions | It does not throw any checked exceptions. However, you get an IndexOutOfBoundsException if try to fetch a value that is out of the bounds. |
Runnable Code:
public class StringBuilderFormattingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Veronica";
int age = 25;
String country = "Canada";
StringBuilder formattedString = new StringBuilder();
formattedString.append("Name: ").append(name).append(", Age: ").append(age).append(", Country: ").append(country);
System.out.println(formattedString.toString());
}
}This code will produce the output: “Name: Veronica, Age: 25, Country: Canada.”
Comparison Java String Formatting Methods
Now, let’s compare the different string formatting methods and discuss which one is most suitable for specific scenarios.
| Method | Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
%s, %d, %f with String.format() | Basic string, integer, and float formatting | Simple and easy to use | Limited control over formatting details |
SimpleDateFormat | Date & time formatting | Precise control over date/time formatting | Requires additional classes and objects |
printf | Stream output, simple formatting | Convenient for simple output | Limited control for complex formatting |
StringBuilder | Complex and efficient formatting | Efficient for concatenating multiple strings | Requires more code for simple cases |
Recommendations
- For simple, quick formatting, such as displaying a message with variables, using
%s,%d, and%fis efficient and straightforward. - When dealing with date & time formatting,
SimpleDateFormatprovides precise control. - If you want to format and print data to the console,
printfis a handy option for straightforward formatting. - For complex formatting scenarios, or when you need to concatenate multiple strings efficiently,
StringBuilderis the way to go.
Before You Leave
String formatting is an essential skill in Java for creating well-structured and human-readable output. You will get to use it in almost every project in Java.
Feel free to copy and paste the code examples into your Java development environment to run and experiment with them.
Before you leave, render your support for us to continue. If you like our tutorials, share this post on social media like Facebook/Twitter.
Happy coding,
TechBeamers.