In this C programming class, we’ll explain the concepts of C variables using flowcharts and code examples. It is one of the core building blocks of C. Hence, please read and understand with full concentration.
What are Variables in C Programming?
In mathematics, a variable means that its value can change, and constant means that its value cannot change.
In C, variables are unique names associated with values. They work as a container and point to a specific location in the program memory.
We can access a C variable directly by its name and also by using the memory address assigned to it.
C Variable Naming Rules
C variables are case-sensitive names. Here are a few simple naming conventions for them.
- A C variable name can include one or more of the following:
- Letters (In both capital and small case)
- Digits from 0 – 9
- Underscore (No other special characters)
- It must either have an underscore or an alphabet as the first character.
- No restriction on the name length but 31 is the max suitable for most of the C compilers.
Check below a few examples of valid and invalid C variable names.
int _count = 5; // valid integer variable int 5th = 5; // error => variable name can't begin with a digit. char choice = '0'; // valid variable name int choice = 0; // error => can't have another variable with the same name.
Type of Variables in C
In C programming, variables are of two types:
- Local,
- Global
Local Variables
Local C variables have a limited scope within the code block delineated with the curly braces. Their placement should happen at the beginning.
The C compiler doesn’t assign a default value to the local variables. Hence, we must provide a value before using them.
The lifetime of a C local variable starts as the execution enters into the code block which is its point of origin and ends after exiting from the same.
However, before learning more about variables, we must cover some basics of data types.
Global Variables
A variable that has a placement in the header section of a C file classifies as global.
The compiler initializes all Global C variables by default as per the following rules.
- An integer variable with 0 as the default value
- The char type with ‘\0.’
- A float type again with 0 as the default
- A pointer with NULL
It remains active and available throughout the execution until it ends.
C Variables Data Types
Data types enable programmers to define variables that can hold the value required by the program or the business logic.
For this class, let’s assume that we’ll only need the following three standard C data types.
Integer (int)
The int represents the integer data type. It can contain positive, negative numbers, and zero. Any other data included in this will give an error.
Floating-point (float)
The float keyword is to define variables that can hold decimal numbers.
Double (double)
The double is another data type like the float. The variables of this type can also hold decimal numbers but provide better accuracy and precision.
That is all we need to learn at this moment. We will see data types from the depth in the upcoming classes.
Now, we will create a pattern here for all programs hereafter. We will see one example in three different ways.
Role of a Flowchart in C
We can understand the workflow of any C program using flowcharts. Let’s know what are they and how can they help.
Purpose of a Flowchart
It is just a visual representation of the functioning of a program created using a pre-defined set of shapes or symbols.
Elements in a Flowchart
The following table should help you in understanding them.
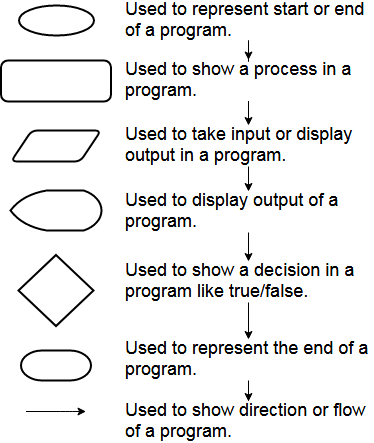
These are just some basic shapes but enough to get us started.
Let’s learn a few essential terms.
- Algorithm: An algorithm is a brief systematic explanation of a program. It just explains the working of a program roughly, not the actual code.
- Pseudo Code: It is the code written in a human-readable language such as English.
Demo of C Variables using Sample Programs
Let us start with a simple program to multiply two numbers.
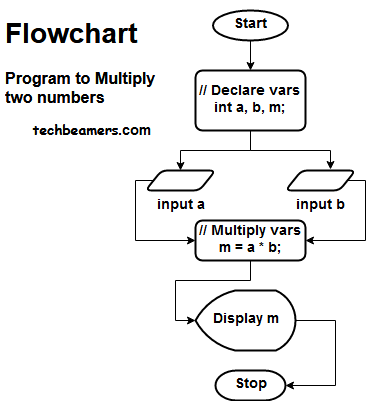
C Program to Multiply Two Numbers
Flowchart & Pseudo Code
Algorithm:
1: Start.
2: Take input from the user for multiplying two numbers.
3: Multiply two numbers (m=a*b)
4: Display output (m)
5: Stop
Coding Snippet
Note: Now there are some keywords, which we will see after this code.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a, b, m;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b);
m= a*b;
printf("The multiplication of %d and %d is %d",a,b,m);
getch();
}Step-by-Step Program Summary
- #include<conio.h>: This header file tells the computer to include console input/output functions. Hence, the term, <conio> stands for console input/output.
- Void main(): It is the primary function in a C program as discussed in the earlier classes.
Note: You have seen us using the int type with the main. The principal difference here is that void means nothing to return whereas the integer type requires the function to return a numeric value. - scanf(): Used to take input from a user. The %d sign is for indicating that the data type is an integer. We will learn more about this in further chapters. The ampersand (&) sign tells the computer that it should store the value of the taken input in that specific address. E.g., &a denotes that the value of the first input will get stored in the location of a.
- getchar(): It tells the program to wait for the reaction of the user. It stands for “Get Character.” The computer holds the output screen for the user to comprehend the output.
The output should come something like this.
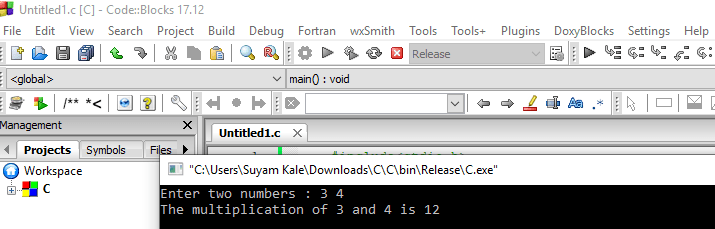
Now we will see an exciting example of how variables work.
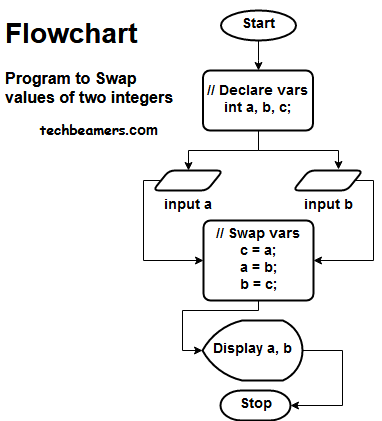
C Program to Swap Two Integers
Flowchart & Pseudo Code
Algorithm:
1: Start
2: Initialize two input variables (a, b) and one for swapping(c).
3: Accept input variables from the user (a & b)
4: Swap the two variables
# Swap variables c=a a=b b=c
5: Display the values before and after swapping.
6: Stop.
Coding Snippet
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b,c;
printf("Enter two numbers to swap : ");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("Values before swapping: %d %d",a,b);
c=a;
a=b;
b=c;
printf("\nValues after swapping: %d %d",a,b);
getchar();
}The output should come something like this-
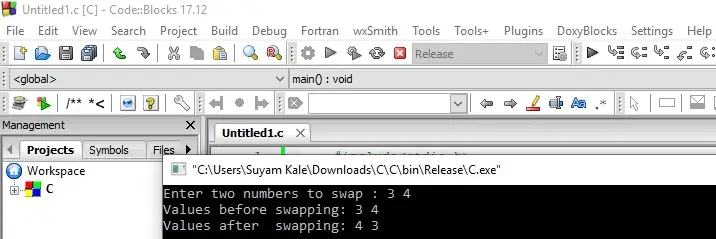
You may have realized that we used a third variable for swapping the values of the two inputs. Can you write a program that can do this without using the third variable? If you can do this, then you will certainly get the idea of how variables literary work. If not, do not worry, another example is available next.
We would recommend that you try very hard on this. It is easy.
Test Exercise on C Variables
Write a program to swap the values of two variables without using a third variable.
Solution:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Enter two numbers to swap : ");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("Values before swapping: %d %d",a,b);
a = a+b;
b = a-b;
a = a-b;
printf("\nValues after swapping: %d %d",a,b);
getchar();
}The output will be the same as the earlier program.
NOTE: We have just covered the basics of variables here. As variables are a bigger topic, we will see it in bits and pieces included in other chapters.