This tutorial provides you with details on how to use operators in Java programs. It is one of the essential topics for you to learn and use in real Java programming.
Learn to Use Operators in Java
The tutorial has the following sections to help you learn quickly.
What are operators in programming?
An operator is a symbol or a character that acts as an inline function.
a) Every operator has a designated action to perform.
b) The operators take inputs from the operands (i.e., variables, an expression, or constants).
c) Some of them work with a single operand (Unary) and some on two (Binary).
What type of operators does Java support?
Java supports a wide variety of operators to manipulate data, generally stored in variables. You can use them to perform operations on variables.
You can perform the operations on hard-coded values too. The following types of operators have support in Java:
a) Arithmetic Operators
b) Logical Operators
c) Bitwise Operators
d) Relational Operators
f) Assignment Operators
g) Shift Operators
h) Unary Operators
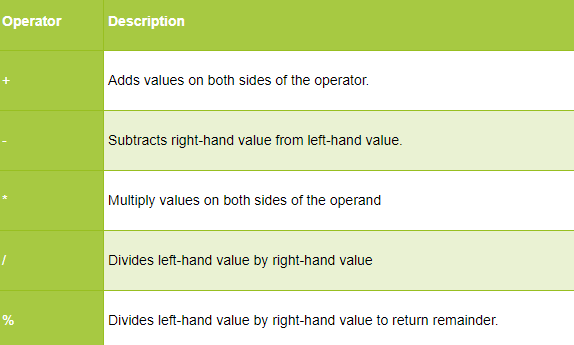
Arithmetic Operators:
As the name signifies, arithmetic operators let you do arithmetic operations on variables of primitive data types.
These include:
· + (Addition) · - (Subtraction) · * (Multiplication) · / (Division) · % (Modulo) To store the remainder after the division of two numbers
Example:
int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = a + b; // var c will be 30 int d = b - a; // var d will evaluate to 10 int e = a * b; // var e will store 200 int f = b / a; // var f will result in 2 int g = b % a; // var g will be 0
Must Read – Data Types in Java
Logical Operators:
You can get these to perform logical AND, NOT, and OR operations, like in digital electronics.
AND and OR, both use binary operands whereas the NOT uses unary.
For AND and OR operators, the compiler skips the second condition if the first evaluates to false. We call it the short-circuiting effect.

Example:
boolean a = true; boolean b = false; boolean c = !a; // var c becomes false, the invert of a boolean d = a && b; // var d will come to false as one of the a and b is false. boolean e = a || b; // var e will come to true as one of the a and b is true.
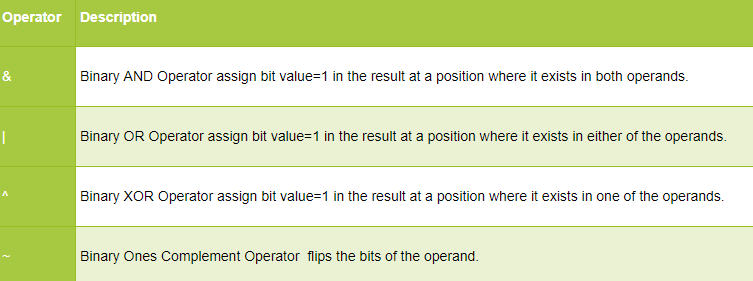
Bitwise Operators:
Bitwise operators provide a mechanism to manipulate the individual bits of a number.
You can use them with integer data types. They include:
& (Bitwise AND) | (Bitwise OR) ^ (Bitwise XOR) ~ (Bitwise Complement)
Example:
int a = 4; int b = 2; int c = a & b; // var c will get a 0 (0000) int d = a ^ b; // var d will get a 6 (0110) int e = a | b; // var e will also get a 6 (0110) int f = ~b; // var f will get a 13 (1101)
Relational Operators:
Relational operators let you perform relations operations like equality, greater than, less than, less than equal to, etc.
They return a boolean value and work on both integer and floating data types.

Example:
int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = 3; int d = a == b; // var d will get to false int e = a < b; // var e will get to true int f = a > b; // var f will get to false int g = c >= b; // var g will get to true int h = c != a; // var h will get to true
Assignment Operators:
Assignment operators let you store the right operand or the result in the left operand.
You can also group it with other operators (generally arithmetic) to form a compound statement.

Example:
int a = 1; // simple assignment int b = 0; b += 2; // compound statement
Shift Operators:
Shift operators make you shift the bits of a number in either direction left or right as per the value mentioned. The operator brings a similar effect as you get from multiplication and division.
These include:
<< (Left shift) To shift the bits of a number to the left >> (Signed Right shift) To shift the bits of a number to the right. The leftmost bit depends on the sign of the initial number. >>> (Unsigned Right shift) To shift the bits of a number to the right. The leftmost bit is set to 0.
Example:
int a = 60; // a gets stroed as 0011 1100 int b = a << 2; // b gets the value 240 (1111 0000) int c = a >> 2; // c gets the value 15 (11111) int d = a >>> 2; // d gets the value 15 (0000 1111)
Unary Operators:
Unary operators need only one operand. Operands are the values that act as input in the operations. These include:
++ Increment by one -- Decrement by one
Example:
int a = 1; // simple assignment int b = a++; // b will become 2 and a will also increment by 1, i.e., 2 int c = a--; // c will evaluate to 1 and a will also decrement by 1 and will become 1
Ternary Operators:
Ternary operators have three operands and are a shorthand version for if-else.
It has the following syntax:
Condition? If true: if false
Example:
int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = a > b ? 3 : 4; // c will get 4 as the result as the condition will turn false. int d = a < b ? 3 : 4; // d will get 3 as the result as the condition will turn true.
instanceof Operator:
This operator provides the ability to check whether an object belongs to a particular class or interface.
It uses the following syntax:
(Object name) instanceof (class/interface type)
After the check, if the object turns out to be of the class or interface type, the operator returns success, i.e., true.
Example:
String val = "Hello"; System.out.print(val instanceof String);
The above statement prints true.
Must Read – Write Your First Java Program
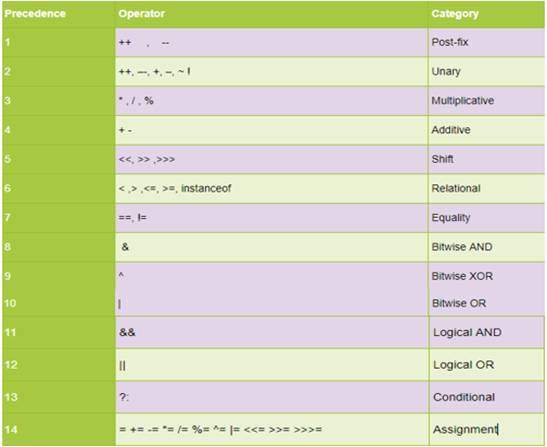
Precedence of Operators:
Operator priority or precedence defines the order for evaluating an expression. It helps in ascertaining which operation to execute first.
The evaluation begins with the operators having a higher priority and after that processes those with lower precedence.
If two operators have the same priority order, then they get assessed from left to right except for the exception of the assignment operator.