From this tutorial, you will be learning about Python decorator. You will understand what decorators are, and how to create and use them with the help of examples.
In Python, decorators are functions that can be used to add functionality to other functions. They are a powerful tool that can make your code more concise and readable. Let’s learn more about them.
Note: The syntax used here is for Python 3. You may modify it to use with other versions of Python.

Read our step-by-step Python tutorial to learn Python from scratch.
What is a Python decorator?
Decorators are a callable entity in Python that allows us to make modifications to functions or classes. The decorator works in an abstract style to extend or completely replace the behavior of an object.
By understanding how to create decorators, you make your code extensible and more readable. Also, you get the functions tailored to your needs without even changing their definitions.
Decorator syntax
Follow the below style:
def decoratorFunc(args):
# Code to you want to execute
...
@decoratorFunc
def existingFunction(args):
# Code that you want to decorate
...Alternatively, you can try this way:
existingFunction = decoratorFunc(existingFunction)
Also Read: Python OrderedDict Tutorial
How does a decorator work in Python?
Mainly, decorators are a construct that wraps a function and gives it a new functionality without changing the original code.
They return the output which may differ from the original behavior of the function.
They are good to use when a function has to operate differently in different situations.
Create your decorator
A decorator is a function that may or may not return a function object.
We place it on top of the function that we want to decorate and pre-fix it with a @ sign.
So, let’s first create the Python decorator function.
def decorator_func(fn):
return 10The above decorator function returns an integer instead of a function.
So when you apply it to a function, it would get overridden altogether.
Check below how to specify a decorator to a function.
@decorator_func
def existing_func():
print("Hello World!")Let’s now bring all the pieces together.
def decorator_func(fn):
return 10
@decorator_func
def existing_func():
print("Hello World!")
existing_func()When you run the above code, the following error occurs.
line 8, in
existing_func()
TypeError: 'int' object is not callableIt is because the decorator replaced the existing function and forced it to return “10” which is an integer, not a callable object in Python.
Note: The decorator’s return value replaces the function, i.e., existing_func.
By the way, if you want to run the function that we decorated, then make the decorator return it. Check the below code.
def decorator_func(fn):
def callExistingFunc():
print("%s was called." % fn)
fn()
return callExistingFunc
@decorator_func
def existing_func():
print("Hello World!")
existing_func()In the above example, our decorator function returns a function that prints the name of the decorated function in Python and executes it.
The result of execution is as follows:
<function existingFunc at 0x0000000000705158> was called. Hello World!
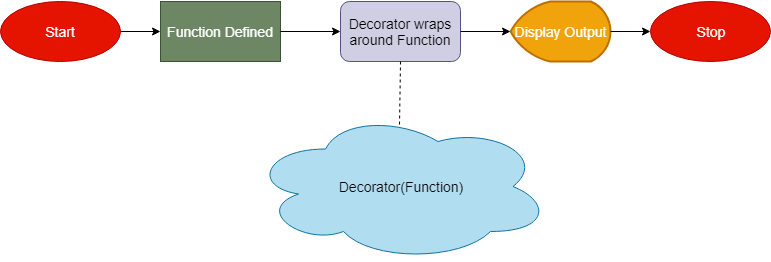
Understanding decorator with a flowchart
The following diagram attempts to simplify the Python decorator concept for you.
Must Read – Functions in Python
Advantages of decorators
- Decorators add functionality to existing functions in Python without modifying the code of the function itself. This can be useful for adding logging, authentication, or other features to a function.
- They make code more concise and readable. Instead of having to write long functions that do multiple things, you can use decorators to break the functionality down into smaller, more manageable pieces.
- They can help change the behavior of a function at runtime. This can be useful for things like caching, throttling, or rate limiting.
Disadvantages of decorators
- Decorators can be difficult to understand for beginners. The concept of decorating a function can be tricky to grasp, and it can be easy to make coding mistakes.
- Decorators can make code more difficult to debug. If something goes wrong with a decorated function, it can be difficult to track down the source of the problem.
- Decorators can be overused. It is important to use decorators sparingly and only when they are really needed.
Chaining decorators in Python code
We can decorate a function as many times as desired. In such a case, the decorators create a chain effect.
Typically, the decorator at the top hands over the control to the next, and continues in this way.
For illustration, check out the following code:
def top(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("1" * 1)
func(*args, **kwargs)
print("1" * 1)
return wrapper
def middle(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("2" * 2)
func(*args, **kwargs)
print("2" * 2)
return wrapper
def bottom(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("3" * 3)
func(*args, **kwargs)
print("3" * 3)
return wrapper
@top
@middle
@bottom
def decorator_demo(anyString):
print(anyString)
decorator_demo("Hello World!")You can check that this example is using three decorators on the decorator_demo() function. Below is the result after execution:
1 22 333 Hello World! 333 22 1
Decorator examples in Python
Let’s now quickly go through some of the Python decorator examples. It is essential to practice with live code to increase your understanding of this concept.
Simple program to demonstrate decorator
def decorate(func):
def first():
func()
print("This is the First Program on Decorators.")
return first
def hello_not_decorated():
print("Hello World!.\n")
print("This is an original function that is not decorated : ")
hello_not_decorated()
print("This is a decorated function :")
@decorate
def hello():
print("Hello World!.")
hello()#1 Output:
This is an original function that is not decorated : Hello World!. This is a decorated function : Hello World!. This is the First Program on Decorators.
Decorate arithmetic operations
def arithmetic_operations(func):
def operators(a, b):
func(a, b)
print("The product is :", a*b)
print("The division is :", a/b)
print("The remainder is :", a%b)
return operators
print("This is a decorated function.")
@arithmetic_operations
def add_and_subtract(a, b):
print("The addition is :", a + b)
print("The subtraction is :", a - b)
add_and_subtract(8, 4)#2 Output:
This is a decorated function. The addition is : 12 The subtraction is : 4 The product is : 32 The division is : 2.0 The remainder is :
Display multiple lines using chaining
def Chaining_of_decorators(func):
print("This is an example of chaining of decorators implementation.")
def Decorator_demo(func):
print("This tutorial is about Decorators.")
print("This is a decorated function.")
@Chaining_of_decorators
@Decorator_demo
def hello():
print("Hello World!")
hello#3 Output:
This is a decorated function. This tutorial is about Decorators. This is an example of chaining of decorators implementation.
Pass arguments to a decorator
def argument_for_decorator(argument1, argument2):
def decorator(function):
def wrapper(*args):
print("%s%s" % (argument1, argument2))
function(*args)
print("Congratulations. You decorated a function.")
return wrapper
return decorator
@argument_for_decorator("Hello ", "World!")
def print_args(*args):
print("The Fibonacci Sequence upto number 8.")
for arg in args:
print(arg)
print_args(1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8)#4 Output:
Hello World! The Fibonacci Sequence upto number 8. 1 1 2 3 5 8 Congratulations. You decorated a function.
Footnote
Finally, you have made it to the end and completed one of the most important topics in Python. This is because many other topics like data classes and Python static methods depend on them.
Let’s now quickly summarize the learning from this tutorial.
- Decorators are functions that take other functions as input and return functions as output.
- Decorators modify the behavior of functions without changing the code of the function itself.
- We use the @ symbol to define them in Python.
- The syntax for a decorator:
@decorator_function(function_to_decorate). - When calling a decorated function, Python first executes the decorator function and then the decorated function is executed.
- Decorators add functionality to functions, such as logging, authentication, or caching.
- They make code more concise and readable.
- They dynamically change the behavior of functions.
We wish the above Python Decorator tutorial would have given you a fair idea of using them in real Python programs.
Best,
TechBeamers