This tutorial will guide you on what is a constructor in Java. You will know how to write a constructor method for a class and instantiate its object.
Constructor in Java
A constructor is a specialized routine which acts as a callback function. It means that you don’t need to call it explicitly. Java invokes it automatically while creating the object of a class.
Its purpose is to initialize an object during its creation. Apart from having the same name as its class, constructors are very much like any other member methods.
Please note that constructors don’t have a defined return type. Usually, you will utilize a constructor to give initial values to the local class variables characterized within the class or to play out some other start-up process required to make a new object.
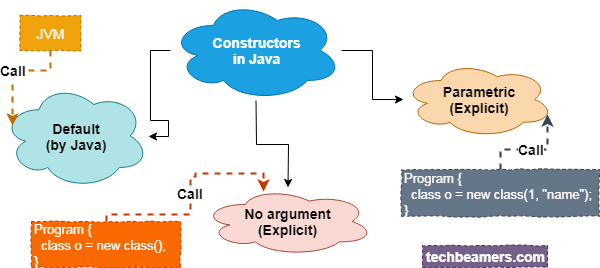
Default constructor
All classes have constructors, regardless of whether you create one or not. Java provides a default constructor for every class. The default constructor sets all member variables to zero.
Notwithstanding, when you create a constructor explicitly, the default constructor doesn’t come into the picture.
Constructor syntax
class className {
// Constructor
className() {
// ...
}
// Other methods…
void method1() {
// ...
}
void method2() {
// ...
}
}When is a constructor called in Java?
Whenever your program creates an object using the new() operator, Java runtime checks whether you have an explicit constructor or not.
If it finds one, then it invokes the user-defined constructor else executes the default one that Java provides.
Check this example:
// Create a TestConstructor class
public class TestConstructor {
int attribute; // Create a class member
// Create an eattributeplicit constructor for the TestConstructor class
public TestConstructor() {
attribute = 1; // Set the initial value for the class attribute attribute
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestConstructor object = new TestConstructor(); // Create an object of class TestConstructor (It'll trigger the constructor)
System.out.println(object.attribute); // Display the result
}
}Output:
1
Types of Constructors
Constructors for Java are mainly of two types:
- Default/No-Argument Constructors
- Parametrized Constructors
No Argument Constructors
This constructor is useful when the programmer does not want to provide any parameters for the object variables or members. With the help of no argument constructors,
- The local variables of the class get initialized,
- The objects or instance variables will have predefined and fixed values.
No Argument Constructor Example
Check out the sample code for the no-argument constructor:
public class NoArgConstructor {
int data;
public NoArgConstructor( /* No Arguments are passed here */) {
data = 100;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NoArgConstructor oj = new NoArgConstructor();
System.out.println("data : " + oj.data);
}
}Output:
data : 100
Parameterized Constructors
When the programmer needs to define new objects with user-defined values or values that change with time, the programmer needs a constructor that accepts these values as one or more parameters from the user or defines them himself.
- We can pass parameters or values to a constructor in a similar way as for any other method.
- Parameters are specified within the parentheses after mentioning the constructor’s name.
Parameterized Constructor Example
Constructors can accept parameters that help to set the attribute values.
Check the below example:
public class Laptop {
int model_year;
String model_make;
String model_name;
public Laptop(int year, String make, String name) {
model_year = year;
model_make = make;
model_name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Laptop myLaptop = new Laptop(2019, "Dell", "Latitude");
System.out.println(myLaptop.model_year + " " + myLaptop.model_make + " " + myLaptop.model_name);
}
}Output:
2019 Dell Latitude
What does a constructor return in Java?
Like other OOP languages, constructors in Java don’t have a return statement to return any user-defined value.
However, they do return the current class instance. Also, it is perfectly alright to add a “return;” statement towards the end of a constructor method.
If you write it before any executable statement, then an unreachable statement error will occur.
public class TestConstructorReturn {
int data;
public TestConstructorReturn( ) {
data = -1;
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestConstructorReturn oj = new TestConstructorReturn();
System.out.println("data : " + oj.data);
}
}Output:
-1
Constructor Overloading in Java
Java allows the overloading of constructors. Its JVM can identify constructors depending on the number of parameters, their types, and the sequence.
See the example below to understand this concept more clearly.
public class ConstructorOverloading {
int a;
double b;
public ConstructorOverloading( ) {
System.out.println("No argument contructor called.");
a = 0;
b = 0.0;
}
public ConstructorOverloading( int a, double b) {
System.out.format("Order (%d, %f) based contructor called.\n", a, b);
this.a = a;
this.b = 0.0;
}
public ConstructorOverloading( double b, int a) {
System.out.format("Order (%f, %d) based contructor called.\n", b, a);
this.a = 0;
this.b = b;
}
public ConstructorOverloading( int value) {
System.out.format("Type (int: %d) based contructor called.\n", value);
this.a = value;
this.b = 0.0;
}
public ConstructorOverloading( double value) {
System.out.format("Type (double: %f) based contructor called.\n", value);
this.b = value;
this.a = 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstructorOverloading o1 = new ConstructorOverloading();
System.out.format("a : %d, b : %f \n\n", o1.a, o1.b);
ConstructorOverloading o2 = new ConstructorOverloading(1, 1.1);
System.out.format("a : %d, b : %f \n\n", o2.a, o2.b);
ConstructorOverloading o3 = new ConstructorOverloading(1.1, 1);
System.out.format("a : %d, b : %f \n\n", o3.a, o3.b);
ConstructorOverloading o4 = new ConstructorOverloading(1);
System.out.format("a : %d, b : %f \n\n", o4.a, o4.b);
ConstructorOverloading o5 = new ConstructorOverloading(1.1);
System.out.format("a : %d, b : %f \n\n", o5.a, o5.b);
}
}Output:
No argument contructor called. a : 0, b : 0.000000 Order (1, 1.100000) based contructor called. a : 1, b : 0.000000 Order (1.100000, 1) based contructor called. a : 0, b : 1.100000 Type (int: 1) based contructor called. a : 1, b : 0.000000 Type (double: 1.100000) based contructor called. a : 0, b : 1.100000