Python range is one of the built-in functions available in Python. It generates a series of integers starting from a start value to a stop value as specified by the user. We can use it with a for loop and traverse the whole range like a list.
Understand Python Range() Function
The range() function takes one required and two optional parameters. It works differently with different combinations of arguments. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the full functionality of the Python range function so that you can easily use it in your programming assignments.
For your information, the scope of this post is to cover the Python 3 range function and its usage. However, it briefly discusses the difference between older range versions (in Python 2).
Syntax of Python range()
There are two variants of the Python 3 range() function. Let’s check their syntaxes one by one.
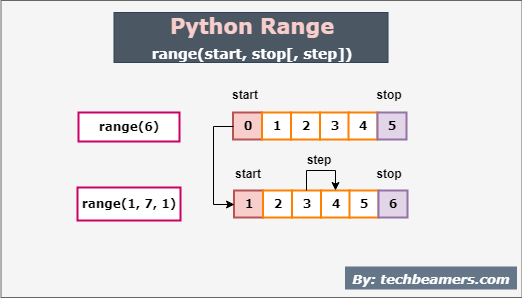
1. range(stop)
It is the most basic form of range(). It takes a single argument to specify the exclusive (stop – 1) upper limit.
‘0’ becomes the starting point here for number generation. See the below example.
robj = range(5) for it in robj: print(it, end = ",") # Result: 0,1,2,3,4,
Check out another example. The range with a ‘0’ stop value generates an empty range, i.e., zero elements.
r = range( 0 ) print( r ) print(len( r )) # Result: # range(0, 0) # 0
If you provide a non-integer stop value, then it raises a TypeError.
range(1.1) # TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
2. range(start, stop[, step])
It is a bit more sophisticated form of the range function. Here, you can generate a series of numbers with a common difference of your choice.
You can pass the following three arguments:
Please note the following points while using range() with the above signature.
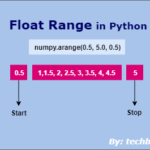
Please note that the range function only accepts integer arguments. To generate a float range, follow the below tutorial.
Must Read: Generate Float Range in Python
Python range() function with examples
Check out the below code examples to understand this function from depth:
Use start, stop and step parameters
# Range with two arguments for it in range(1, 7): print(it, end = ", ") # 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, print() # Range with three arguments for it in range(1, 7, 3): print(it, end = ", ") # 1, 4,
Using the negative start, stop, and step values
We can pass negative values for all range parameters such as the start, stop, and step arguments.
In the below example, we are providing -ve values for the stop and step to iterate the loop in the reverse direction.
# Range with -ve values for it in range(10, -1, -2): print(it, end = ", ") # 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 0
Generate range like an arithmetic series
Let’s produce an arithmetic series (i=10, n=100, d=10) using the range() method.
print(list(range ( 10, 100, 10 ))) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90]
Range() object works as a generator. Hence, we’ve converted it into a list so that we can print the values on demand.
Iterating a list using range()
We can make use of the Python range() function to traverse a list. See the below example.
books = ['python', 'data science', 'machine learning', 'AI', 'deep learning'] size = len(books) for it in range(0, size): print(books[it]) # python # data science # machine learning # AI # deep learning
Convert range to list
Python 3 range() produces a generator object. It fetches values one by one as the loop progresses instead of getting all of them at once.
In reality, the output of the range() function is an immutable sequence of integers. Hence, we can convert the same to a Python list. We’ll use the list constructor to convert range output to a list.
See the below example.
r = range ( 10, 100, 10 ) print(type( r )) # <class 'range'> r = list( r ) print(type( r )) # <class 'list'> print(r) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90]
Make range inclusive
The default nature of Python range() is to exclude the last number. Therefore, it always ignores the upper limit of its output.
However, we can make the following changes in our code to allow it.
- Increment the stop value with the step counter
- Pass the new stop value to the range() function
After making the above changes, let’s see what happens:
start = 0 stop = 7 step = 1 stop = stop + step for it in range(start, stop, step): print(it, end = ", ") # 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Python range vs. xrange()
We’ve outlined a few differences and some key facts about the range() and xrange() functions.
Python 2 used to have two range functions: range() and xrange()
- The difference between the two is that range() returns a list whereas the latter results in an iterator.
In Python 3, we have only one range() function. It is an implementation of the xrange()function from the 2.0 version.
- The new range() function neither returns a list nor an iterator. It gets a new type known as a range object.
- We can iterate on the range object like a list. But it is a little different as we can’t slice it.
- Unlike iterators, which produce one value at a time, the range() function gets all the numbers at once. Hence, it has a high memory requirement.
- However, the range works faster with a small set of numbers.
# Require python 2.x print(type(range(1))) # type 'list' # Require python 2.x print(type(xrange(10))) # class 'xrange' # Require python 3.x print(type(range(10))) # class 'range'
Read more about Python xrange vs. range function.
Using index with Python range output
Yes, range() returns a unique object that has both list and generator-like properties.
Since it acts as a sequence, we can access its elements using the indexes. It allows both +ve and -ve index values.
# Indexing Python range object print(range(0, 7)[1]) # 1 print(range(0, 7)[6]) # 6
Merge output of two range() functions
Python doesn’t have a built-in function to merge the result of two range() objects. However, we can still be able to do it.
There is a module named 'itertools' which has a chain() function to combine two range objects.
See the below example.
from itertools import chain merged = chain(range(5), range(10, 15)) for it in merged: print(it, end = ", ") # 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14
Key Takeaways
Here are some essential facts about the Python range() function: