From this tutorial, you can explore the difference between append and extend methods of Python List. Both these methods are used to manipulate the lists in their specific way.
The append method adds a single or a group of items (sequence) as one element at the tail of a list. On the other hand, the extend method appends the input elements to the end as part of the original list.
After reading the above description about append() and extend(), it may seem a bit confusing to you. So, we’ll explain each of these methods with examples and show the difference between them.
Difference between Append and Extend – Python List
It is quite common for programmers to create and use lists in their programs. However, there might also be situations when they need to extend the existing lists.
Python provides two distinct methods (append() and extend()) to expand lists at runtime. Each of these has some unique characteristics and differences. We are going to highlight them using flowcharts and coding examples.
So, let’s first begin describing the append method.
Python Append()
This method modifies the existing list by appending a single element to the tail. It means that the append() method adds a single element to the list, be it one item or a sequence such as a list, tuple, set, etc.
Below is the Python syntax for the append() method:
# Python append() - List method List.append(number|string|list|tuple|set|dict)
Here, you can see that we can pass one argument of any data type out of a number of supported ones. It could be a singular item (like a number or string) or a sequence (list, tuple, etc.). We have brought a simple diagram representing the Append flow:
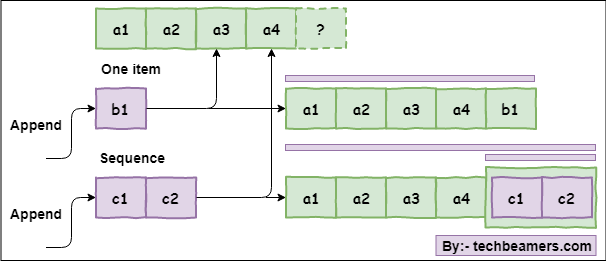
The picture shows two simple use cases: The first appending one item and the second is adding a list with two elements.
It shows that we have an initial list of four elements, say integers. We are then pushing a new number ‘b1’ to the list using the append method.
Since we added a single item, the list now has five elements with ‘b1’ appended at the end. In the second case, the argument is a list of two integers, c1 and c2. Hence, the append() method will add it as one item in the existing list.
You can also see that the output list of the second use case is showing a List within the List.
Below is the sample code to demonstrate these two use cases.
"""
Desc:
Python program to demonstrate list append() function
"""
# Use case#1 - Add a single number to the list
element = 50
# Main list to append new element
in_list = [10, 20, 30, 40]
# Call list append()
in_list.append(element)
# print the output
print("*** Use case#1 ***********")
print("The list: ", in_list)
print("The list size: ", len(in_list))
# Use case#2 - Add multiple numbers to the list
elements = [50, 60]
# Main list to append new elements
in_list = [10, 20, 30, 40]
# Call list append()
in_list.append(elements)
# print the output
print("\n*** Use case#2 ***********")
print("The list: ", in_list)
print("The list size: ", len(in_list))You can copy/paste the above code and run it. You will see the below output.
*** Use case#1 *********** The list: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] The list size: 5 *** Use case#2 *********** The list: [10, 20, 30, 40, [50, 60]] The list size: 5
It is evident from the results that the list grew by one in both use cases. It also proves our point that the append method adds only one element.
Next, let’s unwrap the Python extend() method to know the difference between append and extend functions.
Python Extend()
The extend() method lives up to its name and appends elements at the end of a list.
Unlike append, it only takes an iterable type argument and increases the list length by the number of elements added.
The syntax for the extend() is:
# Python extend() - List method List.append(itereable)
An iterable is a kind of sequence that implements the __iter__() method. And you can iterate through it like for lists, tuples, strings, dictionaries, etc.
Moreover, we have brought a simple diagram representing the Extend function flow:
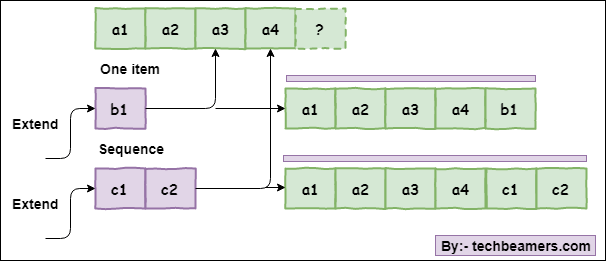
This picture also shows two simple use cases. The first is extending the list by one and another with two elements.
It presents the following facts before us:
- We have an input list of four elements (all integers).
- In the first case, the item to add is a new number b1 using the list extend method.
- When we extend the list by one item, it gets five elements with b1 at the end.
- In the second use case, the argument is a list of two integers, c1 and c2. Hence, the Extend method adds all its items as is in the existing list.
- You can also see that the resultant is a regular list with six elements.
Below is the sample code to demonstrate the above two use cases.
"""
Desc:
Python program to demonstrate list extend() function
"""
# Use case#1 - Extend list by a single element
element = [50] # Note: We can't directly pass a number, it should be an iterable.
# Main list to extend by one element
in_list = [10, 20, 30, 40]
# Call list extend()
in_list.extend(element)
# print the output
print("*** Use case#1 ***********")
print("The list: ", in_list)
print("The list size: ", len(in_list))
# Use case#2 - Extend list by multiple elements
elements = [50, 60]
# Main list to extend by new elements
in_list = [10, 20, 30, 40]
# Call list extend()
in_list.extend(elements)
# print the output
print("\n*** Use case#2 ***********")
print("The list: ", in_list)
print("The list size: ", len(in_list))You can copy/paste the above code and run it. You will see the below output.
*** Use case#1 *********** The list: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] The list size: 5 *** Use case#2 *********** The list: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60] The list size: 6
It is evident from the results that the list grew by no. of new elements in both use cases. It also justifies our point that the Extend method adds all elements to the list.
Summary – Append Vs. Extend
We’ve now seen that both methods grow the list but a little differently. Here, we are summing up the key differences between the append and extend.
- Both extend() and append() are built-in list extension methods.
- Append accepts all data types and adds only one element to the list.
- Extend accepts only iterable types and appends all elements to the list.
We should also consider the difference in their efficiency. The time complexity is the easiest way to assess each method. We are referring to what python.org mentions on their wiki page.
+-----------+-----------------+ | Method | Time Complexity | +-----------+-----------------+ | append() | O(1) | | extend() | O(k) | +-----------+-----------------+
Here, “k” is the number of elements in the iterable parameter of the Extend method.
We hope that after wrapping up this tutorial, you have enough knowledge to define Python Append vs. Extend. However, to learn more about Python, read our step-by-step Python tutorial.