This tutorial explains all MySQL data types, their characteristics, and min, max as well as possible default values. We’ll describe their usages so that you can use them efficiently for creating schemas and tables.
A MySQL table can have one or more fields with specific data types such as a string or date. However, there are more available in MySQL to ease up your job of collecting and storing data.
It is also crucial that you understand which data type should you use and when. Here are some standard goals that define them what do they represent:
1. The data, it is going to hold.
2. The size, it requires that can be static or variable.
3. Is the value of a kind indexable or not?
4. Does this type allow comparison?
MySQL Data Types: A Quick Overview
We can broadly subdivide them into the following types.
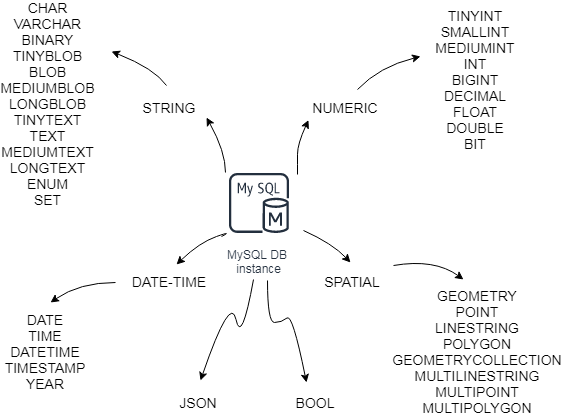
MySQL numeric data types
MySQL provides all usual SQL numeric types that contain: Number data types such as integer, fixed-point, and float.
Moreover, it also supports the BIT data type that can accept bit values. A numeric type can either be signed or unsigned. But the BIT type is a combination of 0s and 1s.
The following is the summary of different numeric types available in MySQL:
INT: A standard integer value that can be +ve and -ve. Its range is from -2147483648 to 2147483647. However, an unsigned int ranges from 0 to 4294967295. It allows width up to 11th place.
TINYINT: A non-regular tiny integer with a range from -128 to 127. It can go up to 255 for +ve only values. It allows width up to four places.
SMALLINT: Another short integer that has a range from -32768 to 32767. It can go up to 65535 for +ve only values. It allows width up to five digits.
MEDIUMINT: This int type has a range from -8388608 to 8388607. It can go up to 16777215 for +ve only values. It allows width up to nine digits.
BIGINT: The largest integer that ranges from -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807. It goes up to 18446744073709551615 for +ve only values. It allows width up to twenty digits.
FLOAT − It is a single-precision decimal number. By default, it allows two decimal places and can hold up to 10 digits. However, you can define a precision of 24 digits.
DOUBLE: It is a double-precision float number. By default, it allows four decimal places and can hold up to 16 digits. However, you can define precision as big as 53.
DECIMAL: It is a fixed-point number, which means that each digit corresponds to one byte.
Boolean
There is not a dedicated type in MySQL for BOOLEAN values. However, it provides the TINYINT to define a boolean. It is the smallest integer type.
Hence, you can also use words like BOOLEAN or BOOL rather than mentioning the type as TINYINT.
String
The MySQL string data type can accept a plain text or binary data (images or data files). You can compare string values, and search substrings using pattern matching. It provides different ways to do that such as LIKE operator, Regex, and simple text lookup. Here is the summary of MySQL string data types:
CHAR: The regular fixed-size string which can hold up to 255 characters. It is right-padded with spaces, and the default size is 1.
VARCHAR: Another regular string type which is variable in length. It can hold up to 255 characters. You should provide the size while specifying a VARCHAR type.
BLOB: BLOB is an acronym that means Binary Large Objects. It allows storage for large-sized binary data, such as pictures or other kinds of files. You can store a maximum of 65535 characters.
TEXT: TEXT field can also take sizable data. While sorting or comparing TEXT type data, the case doesn’t matter. However, BLOB data is case sensitive for these operations. Also, none of the BLOB or TEXT requires to specify the size for creating fields.
TINYBLOB/TINYTEXT: Both of these can accept a maximum of 255 characters as input. And none of the two needs the size with their types.
MEDIUMBLOB/MEDIUMTEXT: Another enhanced version of BLOB/TEXT which can take up to 16777215 characters. Rest of its features are the same as its predecessors.
LONGBLOB/LONGTEXT: It is the largest of all BLOB types with a maximum capacity of 4294967295 characters.
ENUM: It is a list type field which can store multiple elements. It can have NULL values. For example, you can define an ENUM as ENUM (‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’).
SET: This field can take zero or more SET elements.
Date-Time Types
You can have the following MySQL date-time data types:
DATE: It accepts the values in YYYY-MM-DD format. It starts with 1000-01-01 and can go up to 9999-12-31. A simple example is where July 27th, 2019 would appear as 2019-07-27.
DATETIME: It is the combination of a date and time. Its storage format is YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM: SS. It starts with 1000-01-01 00:00:00 and can go up to 9999-12-31 23:59:59. A simple example is where 4:45 in the evening on July 27th, 2019 would appear as 2019-07-27 16:45:00.
TIMESTAMP: It is similar to TIMESTAMP and contains both time and date. It doesn’t include the hyphens separator. A simple example is where 4:45 in the evening on July 27th, 2019 would appear as 20190727164500.
TIME: It is the simplest of the date data types which allow only time as HH:MM: SS.
YEAR: Another date type which takes a year in a 2/4 digit format. The year value goes from (1970 to 2069) or (70 to 69). However, when the length is 4 (default), then it goes from 1901 to 2155.
MySQL spatial data types
MySQL comes with many spatial data types that include some geometrical as well as geographical values.
However, here is the summary of Spatial data types:
GEOMETRY: A spatial value of any kind
POINT: A pair of coordinates (X, Y)
LINESTRING: A linear curve with one or more point
POLYGON: A polygon field
GEOMETRYCOLLECTION: A collection of POINT and LINESTRING values
MULTILINESTRING: A group of many linestrings
MULTIPOINT: A collection of POINT type values
MULTIPOLYGON: A set of POLYGON type values
JSON data type
JSON is a popular acronym for JavaScript Object Notation. We often use this type of data for transferring info between a server and web application.
MySQL supports it since version 5.7.8. It allows you to store and handle JSON data in a better way. It also provides automatic checking of the JSON format.
We hope that after wrapping up this tutorial, you should feel comfortable in using the MySQL TIMESTAMP. However, you may practice more with examples to gain confidence.
Also, to learn SQL from scratch to depth, do read our step by step MySQL tutorial.