In this tutorial, you will discover the insights about the concept of Java Nested Class, also known as Inner Class. There are follow up examples to get into the thick and thin of how can you create and use nested classes.
The major topics covered are:
1. What is Nested Class?
2. Static Nested Class
3. Non-static Nested Class
Let’s check out the detail of Java inner class and their types.
Java Nested Class Overview with Examples
What is a nested class?
In Java, you can create a class inside another one. We term these type of constructs as a Nested Class. this concept help in combining the logic of multiple entities into one. Therefore, you get a higher level of encapsulation and code, which is more maintainable.
Below are some points to note:
- A nested class has to honor the boundaries of its enclosing object.
- It gets access to all public/private members of all classes appearing before it in the chain.
- It implicitly becomes a part (member) of its ancestor in the chain.
- You are free to mark it as private, public, protected, or package-private (default behavior), as needed.
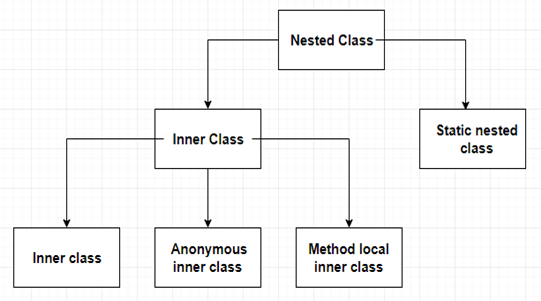
Java has two distinctions in nested classes.
Let’s check out what are these in the subsequent section.
Static Nested/Inner Class
It is a nested class which we declare as static becomes the Static Nested Class. It behaves like a static member of the outer class.
Just like any other static member, this class also doesn’t have any control over instance variables and methods of the outer object. The programmer needs to specify the keyword static to make one such class.
The example below will help you visualize how a static nested class works:
public class Outer{
public void method1() {
System.out.println("This belongs to Outer Class");
}
static class Nested
{
public void method1() {
System.out.println("This belongs to Static Nested Class");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Outer.Nested n = new Outer.Nested();
n.method1();
}
}The syntax to note about is how does the static nested class instantiate. After running the program, the output is:
This belongs to Static Nested Class
Non-static Nested/Inner Class
A non-static nested class happens to be the Inner Class.
The concept of inner classes is of great importance as it provides a security mechanism in Java. As such, we do not have any access to break into a Class once declared with the private access modifier. Therefore, we don’t mark any class as private.
We can achieve this functionality by declaring inner class private. Further, inner classes are of three types depending upon how you use them:
Member level inner class
Java allows us to write a class within a method. It got called as Member-level Inner Class. Note down the following points:
- This class will only be local, and scope remains within the Method.
- This type of inner class instantiates within the defined Method only.
- You can’t create the instances of this class outside the block/method.
The example below shows one such class:
public class Outer {
void method1() {
class InnerClass {
public void msg() {
System.out.println("This is an inner class ");
}
}
InnerClass ins = new InnerClass();
ins.msg();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.method1();
}
}As you would expect, the output of the program after execution is:
This is an inner class
Anonymous inner class
The anonymous inner class is one that has a body with data and functions but does not have a name.
For an anonymous inner class, declaration and instantiation occur at the same time. A programmer may choose to use such a concept for overriding any method of a class or interface.
The example below shows its demo:
abstract class AnonClass {
public abstract void method1();
}
public class Outer {
public static void main(String args[]) {
AnonClass ac = new AnonClass()
{
public void method1() {
System.out.println("This is an anonymous class");
}
};
ac.method1();
}
}The keyword Abstract makes sure the class is available w/o body. Similarly, for the method1, it makes sure the method is just a declaration. We’ll override it in the Main function.
After running the code, the output comes as:
This is an anonymous class
We can also use an anonymous class as an argument to a method. Simultaneously, we can utilize it to override the predefined function of the Inner Class.
The example below helps you visualize the above facts:
class Prev {
void simplePrint() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
class Next {
int x = 10;
Prev prev = new Prev() {
void simplePrint() {
System.out.println("HELLO " + x);
}
};
void print() {
prev.simplePrint();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Next next = new Next();
Prev prev = new Prev();
next.print();
prev.simplePrint();
}
}This program overrides simplePrint function in Prev class. Whatever you define within the anonymous class remains in the scope of the instance of the inner class only (prev in this case).
We cannot create a new method within this instance as long as the same is not available in the Prev class initially. This case is similar to implementing an interface.
Please note that the anonymous class doesn’t permit a constructor declaration within.
After the execution, the output of the program is:
HELLO 10 hello
Local inner class
In Java, we can create a class inside a method which will have localized scope. Hence, it got called a Local Inner Class.
Its scope will be bound to the method. Also, we can instantiate it only in the body of its host.
Moreover, we can set it as private, unlike the usual way. If declared private, then we won’t be able to access it from outside.
The example below shows a local inner class:
class Outer {
class Inner {
public void meth() {
System.out.println("Inner class");
}
}
void print() {
Inner inner = new Inner();
inner.meth();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Outer outer = new Outer();
outer.print();
}
}After you run the program, the output comes as:
Inner class
Inner Classes are generally private by nature, unlike the case discussed above. Moreover, these inner classes can be useful in accessing Private Members of the outer class.
See the below example:
class Outer {
private int num = 10;
public class Inner {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Private number access from inner class " + num);
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Outer out = new Outer();
Outer.Inner in = out.new Inner();
in.print();
}
}To execute the above code, you may have to save it as Test.java. Anyways, after running the program, it gets you the following output:
Private number access from inner class 10
We hope this tutorial on Java nested class (inner class) would have helped you figure out how it works in Java. Please do practice with the examples to get full clarity.